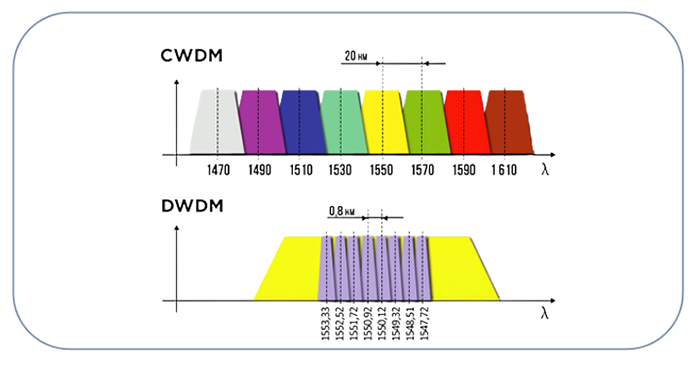
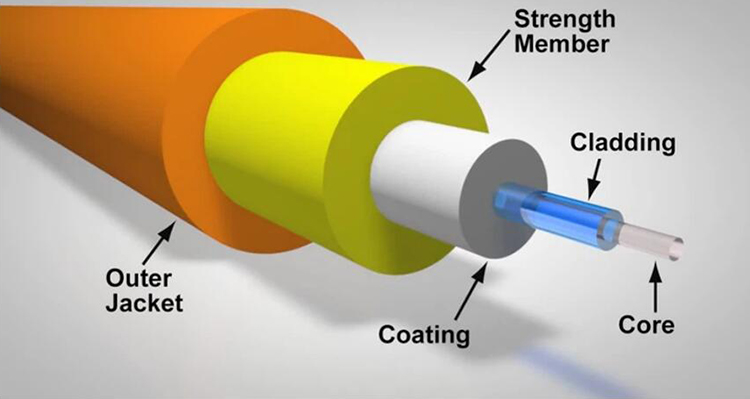
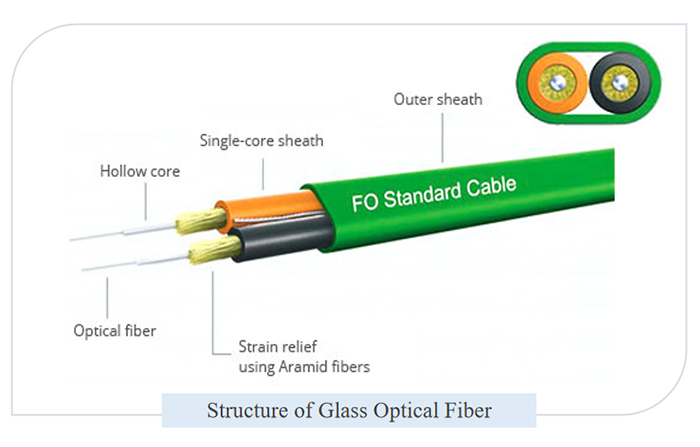
In an era marked by the insatiable hunger for data, we often take for granted the unsung heroes that enable our connected world. Beneath the bustling streets of our cities and concealed within the unassuming data centers, a technological marvel quietly revolutionizes the way we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves. This marvel is none other than the humble yet extraordinary Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable.
As we navigate the digital landscape, these unobtrusive cables transport an astronomical volume of information at the speed of light. They underpin the foundation of our modern society, allowing us to browse the web, stream high-definition content, engage in crystal-clear video conferences, and access cloud services seamlessly. Yet, despite their critical role, the Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable often remains hidden from view, known only to those in the inner circles of the telecommunications and data center industries.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables, shining a spotlight on the unsung champions of our digital age. We’ll explore the inner workings of these cables, delving into their unique design and the science that powers them. We’ll uncover the multitude of advantages that set them apart from conventional optical cables and examine their diverse applications across various sectors.
Moreover, this guide serves as a tribute to the engineers, technicians, and visionaries who have tirelessly worked to refine and advance Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables over the years. It’s a testament to the unyielding human spirit of innovation and progress, which has brought us to a point where we can transmit vast troves of data with unparalleled efficiency.
So, whether you’re a seasoned professional in the field, an aspiring tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the invisible highways that connect our digital world, prepare to be captivated. The Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable is a remarkable fusion of science and engineering, an enabler of dreams and possibilities. Join us as we embark on a journey of discovery, demystifying the technology that has changed the way we connect and communicate. Welcome to the world of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables, where light illuminates the path to our connected future.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable?
A Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable is a specialized type of optical fiber cable designed to accommodate multiple individual optical fibers within a single, flat ribbon-like structure. Instead of having each optical fiber individually insulated and protected, ribbon cables typically have several optical fibers laid side by side and enclosed in a common outer sheath or jacket. This flat ribbon design is a distinctive feature of these cables.
Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables are known for their high fiber density, making them ideal for applications where space efficiency and the ability to transmit a large volume of data are crucial. They are commonly used in telecommunications networks, data centers, and other environments where efficient cable management and high-speed data transmission are essential. Ribbon cables are often preferred for their ease of mass fusion splicing, which speeds up installation and maintenance processes, and they come in various structural variations to meet specific application needs.
What is the Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable Structure?
There are generally three main structural variations of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
Layer Stranded: In Layer Stranded Ribbon Cables, optical fibers are arranged in multiple layers within a single ribbon. This design optimizes fiber density while maintaining flexibility. It is commonly used in various applications where high fiber counts and efficient cable management are essential.
Skeleton Type: Skeleton Type Ribbon Cables feature a central supporting member, often referred to as a “skeleton,” which holds the optical fibers in place. This design provides added protection and stability to the fibers, making it suitable for situations where enhanced fiber protection is required.
Central Tube: Central Tube Ribbon Cables house optical fibers within a central tube, similar to the structure of traditional loose-tube cables. This configuration balances fiber protection with efficient use of space, making it a versatile choice for a range of applications.
These different structural variations allow Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables to meet various requirements in terms of fiber density, protection, and flexibility, making them adaptable to different usage scenarios.
Advantages of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
Rapid Installation and Maintenance:
One of the standout features of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables is their ease of installation and maintenance. Traditional fiber cables with individual round fibers can be time-consuming to splice, requiring meticulous alignment and fusion splicing for each fiber. In contrast, Ribbon Fiber Cables simplify this process. Multiple fibers are pre-aligned and encapsulated within the flat ribbon structure. This design significantly reduces the time and labor required for installation and maintenance tasks. As a result, telecom operators, data center managers, and technicians can complete projects more efficiently, saving both time and resources.
High Fiber Density:
Perhaps the most striking advantage of Ribbon Fiber Cables is their exceptional fiber density. These cables can house a remarkable number of optical fibers within a single flat ribbon, often exceeding the capacity of round cables of the same size. This high fiber density is particularly advantageous in scenarios where space is limited, such as densely populated urban areas or congested data center environments. The ability to transmit vast amounts of data through a compact cable is a game-changer, enabling the expansion of high-speed internet services and the efficient use of infrastructure.
Efficient Cable Management:
Effective cable management is a critical consideration in data centers, telecom facilities, and even in building networks. Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables excel in this regard. Their organized, flat design makes cable routing, labeling, and organization straightforward. With Ribbon Cables, technicians can easily identify and manage individual fibers, reducing the risk of errors and simplifying maintenance procedures. Neatly arranged cables also improve airflow and cooling in data center environments, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Cost-Efficiency:
The cost-effectiveness of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables extends beyond their installation and maintenance advantages. The reduction in labor hours required for splicing and cable management translates to cost savings. Additionally, the higher fiber density allows network operators to maximize the use of existing infrastructure, delaying the need for costly infrastructure expansions. This efficiency in resource utilization makes Ribbon Fiber Cables a financially sound choice for telecom companies and data center operators seeking to optimize their investments.
High Fiber Count Options:
In the world of fiber optics, versatility is key. Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables are available in various configurations, including options with a remarkably high fiber count. These cables can support a substantial number of optical channels, making them suitable for applications that demand extensive bandwidth, such as long-distance data transmission, backbone networks, and high-capacity data centers. With Ribbon Fiber Cables, network architects have the flexibility to design and implement systems that meet the ever-increasing demands for connectivity and data transfer.
These advantages collectively make Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables a versatile and indispensable component of modern communication networks. Their design innovations and efficiency improvements have transformed the way we transmit data, enabling the high-speed, high-capacity connections that power our interconnected world.
While Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables offer numerous advantages, they are not without their disadvantages. It’s essential to consider both the pros and cons when evaluating their suitability for specific applications.
Here Are Some Potential Disadvantages of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
Higher Complexity for Individual Fiber Access: Ribbon Fiber Cables house multiple optical fibers in a single ribbon, which can make it more challenging to access and repair individual fibers if a problem arises. Unlike traditional loose-tube cables, where each fiber is individually protected and accessible, repairing a specific fiber within a ribbon may require separating and re-splicing the entire ribbon, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Less Flexibility: Ribbon Fiber Cables are typically less flexible than loose-tube cables or round fiber cables. This reduced flexibility can make them less suitable for applications where the cable needs to bend sharply or navigate tight corners.
Potential for Ribbon Damage: Because the fibers are closely packed within a ribbon, there is a risk that the entire ribbon could be damaged if the cable is bent or kinked beyond its specified bend radius. This risk can be mitigated with proper cable handling and installation techniques, but it’s an important consideration.
Complexity in Identifying Individual Fibers: While efficient cable management is an advantage of ribbon cables, it can also present challenges when it comes to identifying and tracing individual fibers within a ribbon, especially in large-scale installations. Proper labeling and documentation are crucial to overcome this challenge.
Limited Compatibility: Ribbon Fiber Cables may not be compatible with all types of optical connectors and splicing equipment. Compatibility issues could arise when connecting ribbon cables to devices or equipment designed for single fibers.
Initial Cost: While Ribbon Fiber Cables can lead to long-term cost savings due to their efficiency, the initial purchase cost may be higher compared to traditional loose-tube cables. Organizations should consider the overall cost of ownership and the specific needs of their network.
It’s important to note that these disadvantages may not be significant drawbacks in many applications, and Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables continue to be a preferred choice for high-density and high-capacity optical networks. The choice between ribbon cables and other fiber optic cable types should be based on a thorough assessment of the specific requirements and constraints of the project.
Certainly, Let’s Explore an Extended List of Applications for Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables, Showcasing Their Versatility Across Various Industries:
- Telecommunications Networks:
Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables serve as the backbone of telecommunications networks, enabling high-speed data transmission, voice communication, and video streaming services. They support the ever-increasing demand for bandwidth in both urban and remote areas
- Data Centers:
Data centers rely heavily on Ribbon Fiber Cables to connect servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. Their high fiber density and efficient cable management are crucial for maintaining the uninterrupted flow of data within these mission-critical facilities.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
ISPs use Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables to provide residential and commercial customers with high-speed internet connections. These cables enable faster data transfer rates and support the growing demand for broadband services.
- Long-Distance Data Transmission:
Ribbon Fiber Cables are employed in long-haul and submarine cable systems, where they transmit data over vast distances. Their high fiber count and efficient splicing make them ideal for such applications, connecting continents and facilitating global communication.
- Healthcare and Medical Imaging:
In healthcare, Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables enable high-resolution medical imaging systems, such as MRI and CT scans. They ensure the rapid and reliable transmission of medical data for diagnostics and patient care.
- Military and Defense:
Military and defense applications often require secure and high-capacity communication networks. Ribbon Fiber Cables play a vital role in ensuring the efficient exchange of information in these critical environments.
- Broadcast and Entertainment:
The media and entertainment industry relies on Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables for transmitting high-definition video, audio, and data signals in live broadcasting, video production, and multimedia applications.
- Industrial Automation and Control:
In industrial settings, Ribbon Fiber Cables support high-speed data transmission for automation, control systems, and industrial IoT applications, ensuring efficient and real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes.
- Research and Education:
Educational institutions and research facilities use Ribbon Fiber Cables to establish high-speed networks for data sharing, collaborative research, and educational resources. They are essential for connecting campuses and facilitating remote learning.
- Smart Cities and IoT:
– Ribbon Fiber Cables contribute to the development of smart city infrastructure by supporting the deployment of sensors, cameras, and IoT devices. They enable efficient data collection and analysis for improved urban management.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
– In remote and challenging environments such as oil rigs and pipelines, Ribbon Fiber Cables ensure reliable data communication for monitoring and controlling operations, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Transportation and Aviation:
– Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables are used in transportation systems, including high-speed trains and airports, to support communication, security, and passenger information systems.
- Financial Services:
– Financial institutions rely on secure and high-speed networks for stock trading, data analysis, and secure transactions. Ribbon Fiber Cables are instrumental in maintaining the integrity and speed of financial networks.
- Research and Development Labs:
– Research labs depend on high-capacity data transmission for experiments, simulations, and data analysis. Ribbon Fiber Cables facilitate the rapid exchange of data within scientific and research communities.
- Renewable Energy:
– In wind and solar farms, Ribbon Fiber Cables are used for data transmission and control systems to monitor and optimize energy production.
These diverse applications showcase the adaptability and significance of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables across multiple industries, where efficient data transmission is crucial for innovation, connectivity, and progress.
Installation of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
Proper Cable Handling:
Before installation, it’s crucial to handle Ribbon Fiber Cables with care. Avoid excessive bending, twisting, or kinking, as this can damage the fibers or the ribbon structure. Use appropriate cable reels and pay attention to the manufacturer’s guidelines for handling.
Cable Routing Planning:
Plan the cable routing carefully, considering factors like bend radii, cable tray and conduit size, and avoiding sharp turns. Ribbon cables are less flexible than loose-tube cables, so ensuring smooth, gradual bends is essential to prevent stress on the fibers.
Splice Enclosures and Patch Panels:
Ribbon Fiber Cables are typically spliced and terminated in splice enclosures and patch panels. Ensure that these components are clean, well-organized, and labeled properly. Efficient cable management in these enclosures is crucial for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fusion Splicing:
Fusion splicing is the process of joining optical fibers together. Ribbon cables offer the advantage of mass fusion splicing, where multiple fibers can be spliced simultaneously. Employ experienced technicians and use fusion splicing machines that are compatible with ribbon fiber splicing to ensure accurate and reliable connections.
Fiber Testing and Quality Assurance:
After splicing and installation, perform thorough fiber testing using optical time-domain reflectometers (OTDRs) or optical power meters. Testing helps identify any issues like splice losses, breaks, or bends that may affect signal quality. Address and rectify any problems to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
Regular Inspections:
Implement a routine inspection schedule to check the condition of Ribbon Fiber Cables, splice enclosures, and connectors. Look for signs of physical damage, such as kinks or bends exceeding the specified limits. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Cleaning and Dust Control:
Keep connectors and splice enclosures clean to prevent signal degradation due to dirt, dust, or contaminants. Use lint-free cleaning materials and optical-grade cleaning solutions. Dust caps should be used to protect unused connectors.
Documentation and Labeling:
Maintain accurate documentation of cable routes, splice locations, and connector types. Proper labeling of fibers and enclosures simplifies troubleshooting and minimizes the risk of errors during maintenance and upgrades.
Repairs and Splicing:
In the event of a cable break or fiber damage, Ribbon Fiber Cables may require splicing or repairs. Trained technicians should perform these tasks to ensure minimal signal loss and maintain the cable’s performance.
Testing and Certification:
Periodic testing and certification of optical fibers help verify that the network continues to meet performance standards. Certifying the cables ensures that they can reliably support the required data rates and bandwidth.
Future-Proofing and Upgrades:
Stay informed about advancements in fiber optic technology. As network demands evolve, consider upgrading or expanding your Ribbon Fiber Cable infrastructure to accommodate higher speeds and capacities.
Disaster Preparedness:
Have a disaster recovery plan in place. Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables are often critical for emergency communication and data transmission. Redundancy and backup systems can help ensure network resilience during unforeseen events.
By adhering to best practices during installation and conducting regular maintenance, organizations can maximize the longevity and performance of their Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable infrastructure, ensuring that it continues to support the high-speed data transmission demands of today’s digital world.
Future Trends of Ribbon Fiber Optic Cable:
However, please note that technological trends can evolve rapidly, so it’s essential to stay updated with the latest developments. Here are some future trends and possibilities for Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables:
- Increased Fiber Capacity: The demand for higher bandwidth continues to grow with the increasing use of data-intensive applications, IoT devices, and emerging technologies like 5G and 6G. Future Ribbon Fiber Cables may incorporate even more optical fibers to support these expanding bandwidth requirements.
- Enhanced Data Rates: Advancements in fiber optic technology may lead to higher data transmission rates. Ribbon Fiber Cables may play a critical role in supporting the ultra-high-speed data transfer needed for emerging applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and real-time 8K video streaming.
- Advanced Materials: Researchers are continually working on developing new materials for optical fibers to reduce signal loss and improve overall performance. Future Ribbon Fiber Cables may benefit from these material advancements, leading to more efficient data transmission.
- Miniaturization: Smaller, more compact Ribbon Fiber Cables may become available, allowing for easier installation in space-constrained environments. This could be particularly important in urban areas and retrofitting existing infrastructure.
- Improved Bend Resistance: Ribbon Fiber Cables may become more resilient to bending and twisting, reducing the risk of signal loss or damage. This feature could be crucial for applications where cables need to navigate tight spaces or sharp corners.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables are likely to play a significant role in the deployment of emerging technologies such as smart cities, the Internet of Things (IoT), and autonomous vehicles. These applications will require robust and efficient data transmission networks.
- Green and Sustainable Solutions: As environmental concerns grow, there may be a push for more eco-friendly cable designs and manufacturing processes. Ribbon Fiber Cables could see innovations aimed at reducing their environmental footprint.
- Security Enhancements: With the increasing importance of data security, Ribbon Fiber Cables may incorporate features to safeguard against data breaches, including improved encryption and secure cable management.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Ongoing research and development efforts may lead to more cost-effective manufacturing techniques for Ribbon Fiber Cables, making them accessible for a broader range of applications and industries.
- Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) Expansion: As demand for high-speed internet in residential areas continues to rise, Ribbon Fiber Cables may be used to extend fiber-optic connections directly to homes, enhancing internet speeds and reliability.
To stay informed about the latest trends and developments in Ribbon Fiber Optic Cables, it’s essential to follow industry news, attend relevant conferences, and engage with experts in the field. Additionally, regular updates from manufacturers and industry organizations will provide insights into the evolving landscape of fiber optic technology.