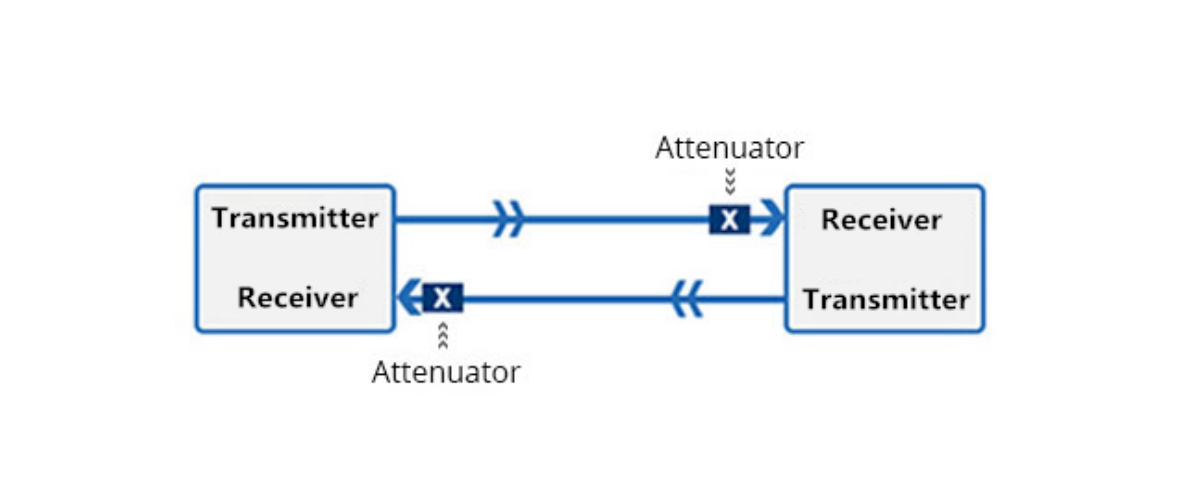
Fiber optic communication has revolutionized the way we transmit data over long distances, enabling high-speed internet, clear voice calls, and seamless video streaming. Yet, in the world of optics, not everything is about boosting signal strength. Sometimes, you need to rein it in. This is where fiber optic attenuators come into play. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamental principles behind fiber optic attenuators and provide you with expert insights on how to select the right type for your specific needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Fiber Optic Attenuators
Principles of Fiber Optic Attenuators
Before diving into the selection process, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles that govern fiber optic attenuators:
- Attenuation Mechanism
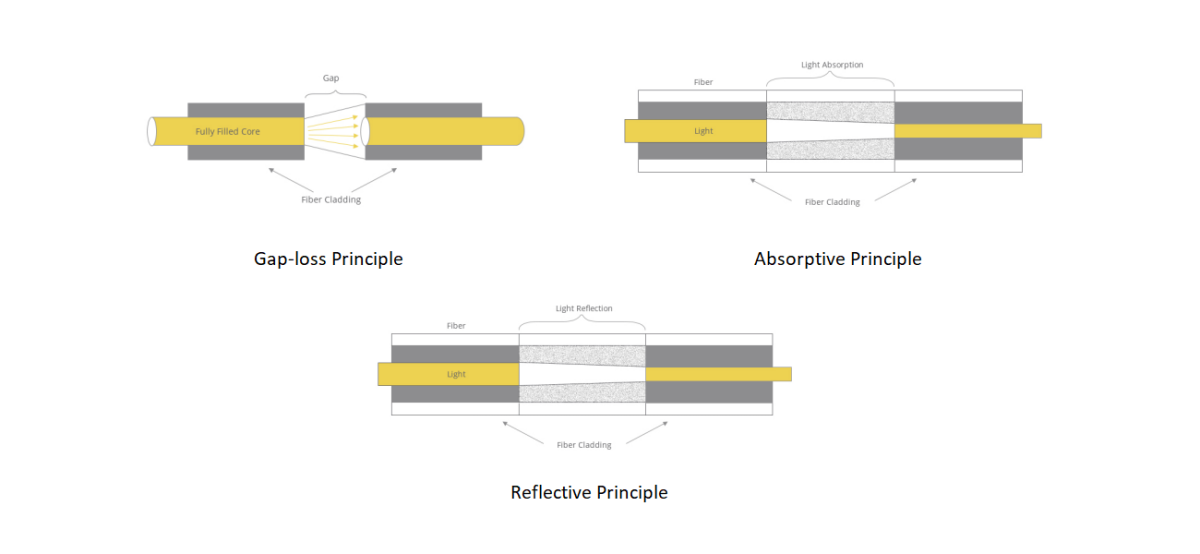
Fiber optic attenuators operate on the principle of reducing the intensity of transmitted light signals. They achieve this by employing one of three primary attenuation mechanisms: absorption, scattering, or reflection. Absorption attenuators are the most common, where a portion of the optical power is converted into heat within the attenuator material, thus reducing the signal strength.
- Material Matters
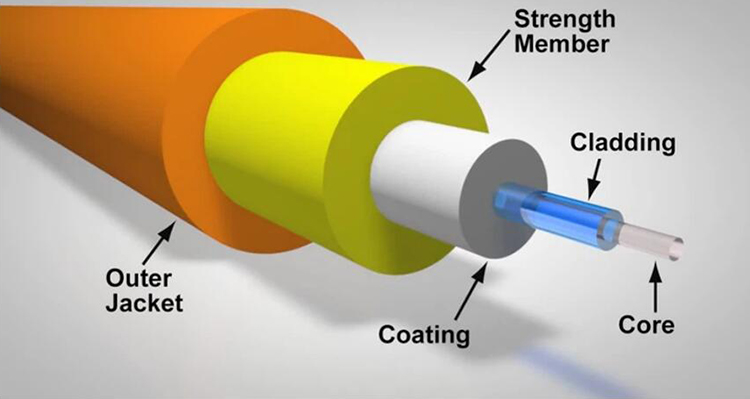
The core material of an attenuator plays a pivotal role in its performance. Typically, attenuators use doped fiber, which contains rare earth elements like erbium or ytterbium. These elements are strategically doped into the fiber to absorb light at specific wavelengths, making them ideal for precise attenuation control.
- Fixed vs Variable Attenuators
Fiber optic attenuators come in two main flavors: fixed and variable. Fixed attenuators provide a predetermined, constant level of attenuation, while variable attenuators offer adjustable levels of attenuation. The choice between the two depends on the flexibility and precision required for your specific application.
- Connector Compatibility
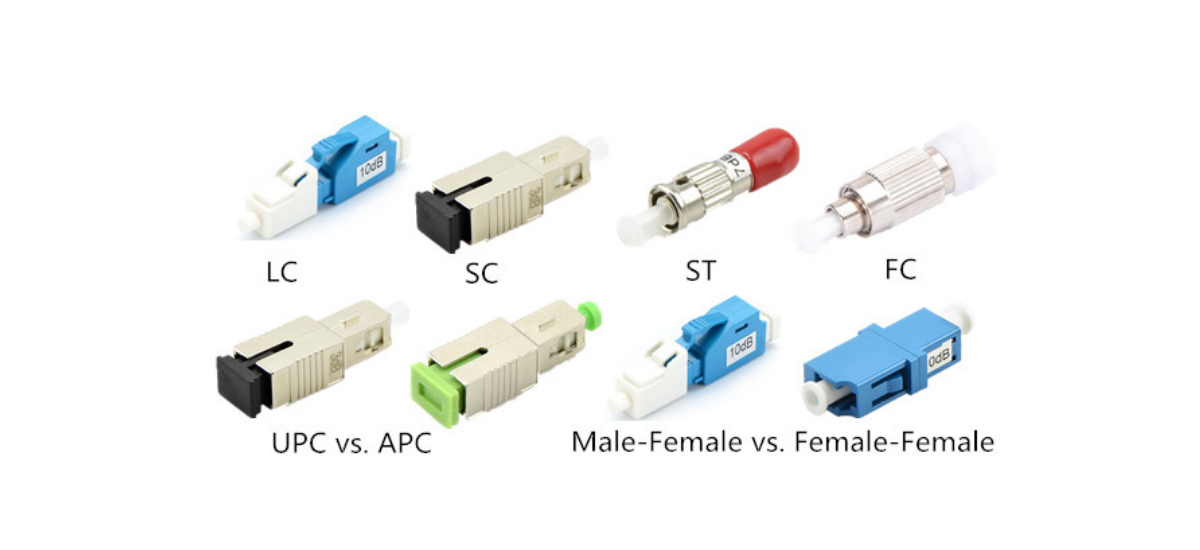
Attenuators are available in various connector types, such as SC, LC, and ST. It’s crucial to select an attenuator that’s compatible with your existing optical network to ensure seamless integration.
- Wavelength Compatibility
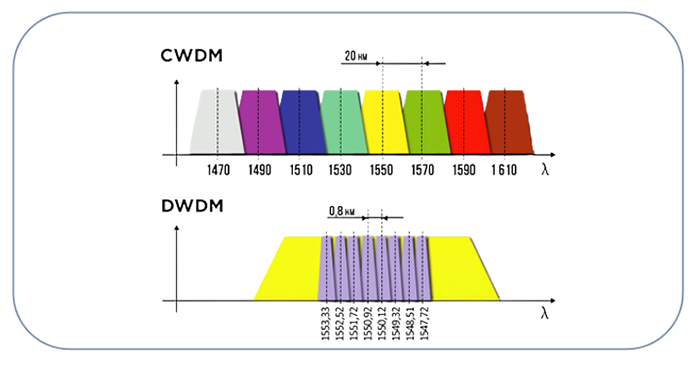
Consider the wavelengths of the signals within your optical system. Attenuators are designed for specific wavelength ranges, so choose one that aligns with your system’s requirements to achieve optimal attenuation.
Selecting the Right Type of Attenuator
Now that we’ve covered the principles let’s delve into the selection process for fiber optic attenuators:
- Application-Specific Attenuators
Different applications demand varying levels of attenuation precision. For instance, testing and measurement applications may require highly precise attenuators, while simple signal adjustments may suffice for other purposes. Tailor your choice to your specific application.
- Determine the Desired Attenuation Level
The level of attenuation required is a critical factor. Fixed attenuators come in predefined attenuation values, usually measured in dB (decibels). Variable attenuators, on the other hand, allow you to fine-tune the attenuation level within a specified range. Carefully assess your needs and select accordingly.
- Connector Compatibility is Key
Ensure that the attenuator’s connector type matches your existing fiber optic network. Mismatched connectors can lead to signal loss and degradation, so meticulous attention to compatibility is paramount.
- Wavelength Compatibility
As mentioned earlier, the wavelength of your signals is crucial. Make sure the attenuator is optimized for the specific wavelengths in your system. Some attenuators are designed for specific wavelength ranges, so thorough compatibility checking is essential.
- Budget Considerations
Cost is always a factor. Variable attenuators typically come with a higher price tag than fixed ones due to their flexibility. Consider your budget alongside the level of flexibility your network requires to make an informed decision.
- Environmental Conditions
If your network operates in challenging environmental conditions, opt for attenuators designed to withstand these challenges. Factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or moisture should be taken into account.
Advanced Features and Specialized Attenuators
Polarization-Maintaining Attenuators
In scenarios where maintaining polarization is crucial, polarization-maintaining attenuators come to the rescue. They ensure that the input light’s polarization state is preserved even after attenuation, making them indispensable for polarization-sensitive systems.
In-line vs Bulkhead Attenuators
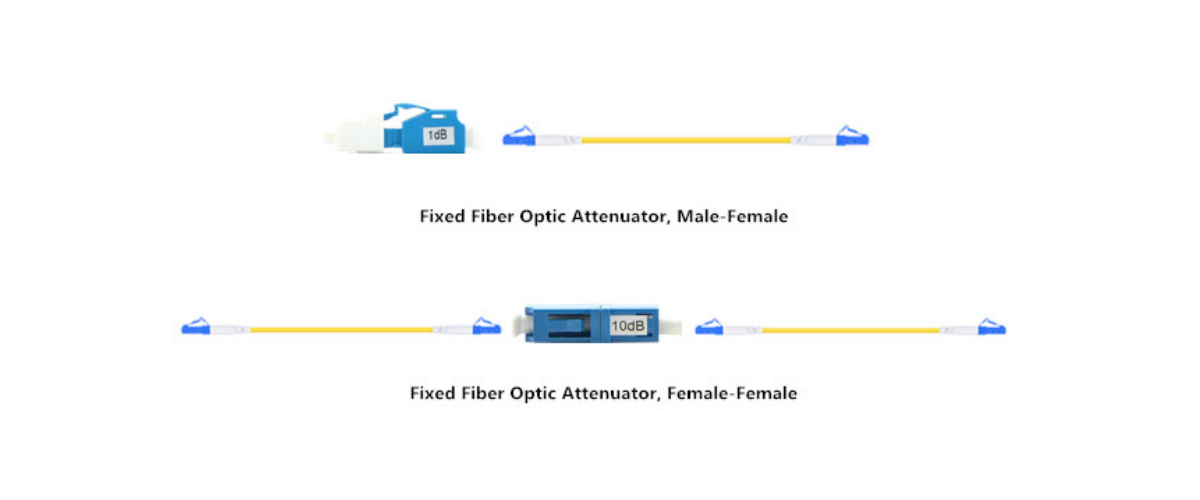
Attenuators are available in different form factors, including in-line and bulkhead variants. In-line attenuators are inserted directly into the fiber optic link like a connector, while bulkhead attenuators are designed for mounting onto panels or walls. Choose the form factor that best suits your installation requirements.
Fiber Type and Mode
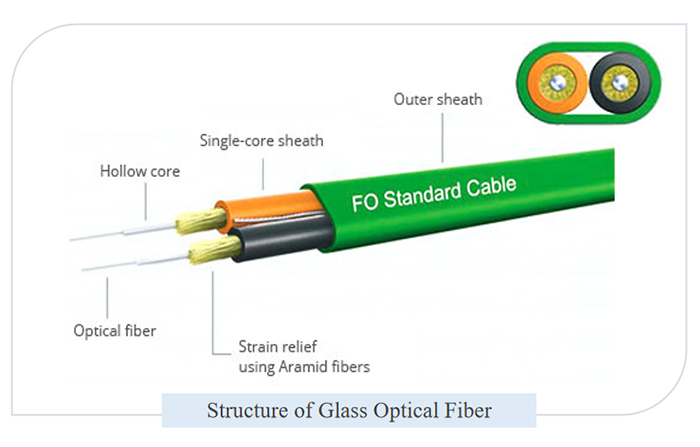
The type of fiber used in your network is critical. Single-mode and multi-mode fibers have different core diameters, which can impact attenuation characteristics. Ensure that your attenuator is compatible with the specific type and mode of fiber in your system.
Return Loss Considerations
Apart from reducing signal strength, some attenuators may introduce reflections back into the network. These reflections can cause interference and signal degradation. Attenuators with low return loss specifications are preferred, particularly in high-performance applications where signal quality is paramount.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Precise Installation Techniques
When installing an attenuator, ensure that it is securely connected and precisely aligned with the fiber optic connectors. Even slight misalignment can lead to additional signal loss and reduced network performance.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Like all optical components, attenuators require periodic inspection and cleaning. Dust, dirt, and contaminants can accumulate on the attenuator’s surface, resulting in increased attenuation. Utilize proper cleaning tools and techniques to maintain optimal performance.
Calibration and Testing
For applications where precise attenuation levels are critical, consider calibrating your attenuators at regular intervals. This ensures that they consistently provide the specified level of attenuation, maintaining the accuracy of your optical measurements.
Conclusion
Fiber optic attenuators are the unsung heroes of optical communication networks, allowing for precise control over signal strength when needed. To harness their benefits, it’s imperative to understand the principles governing their operation and to make informed decisions when selecting the right type for your network.
By considering factors such as your specific application, desired attenuation level, connector compatibility, wavelength requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions, you can make choices that lead to improved signal quality, reduced signal degradation, and enhanced overall network performance.
Remember, a well-chosen attenuator can make a significant difference in the efficiency and reliability of your optical network. Take the time to evaluate your requirements and select the attenuator that aligns perfectly with your goals.