800G optical modules have entered mass production this year, driven by the surge in demand from technologies like ChatGPT and other AI advancements. This note provides an overview of the information on 800G optical modules for your reference.
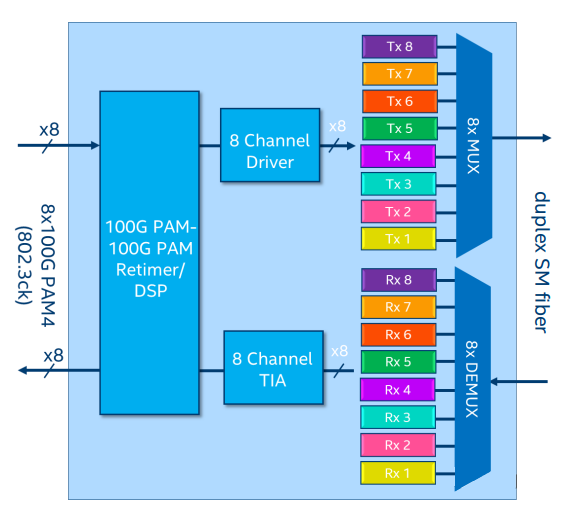
800G = 8 * 100G = 4 * 200G. Therefore, based on the single-channel rate, 800G optical modules can mainly be divided into two categories: single-channel 100G and 200G. The corresponding architectures are illustrated below. Single-channel 100G optical modules can be implemented more quickly, whereas 200G requires higher performance optical components. Currently, the maximum rate supported at the electrical interface is 112Gbps PAM4. For single-channel 200G, a gearbox is required for conversion.
For multimode scenarios, there are mainly two 800G optical module standards for transmission distances under 100 meters.
Table of Contents
Toggle1) 800G SR8
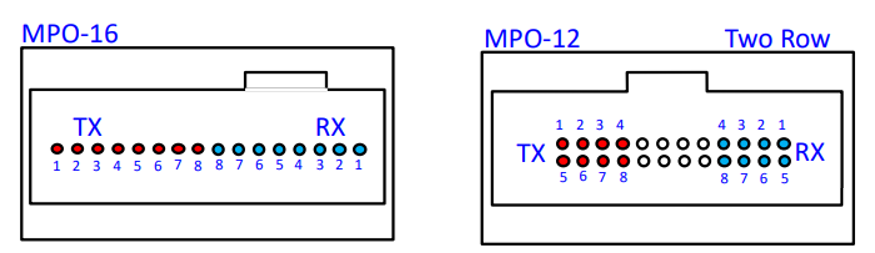
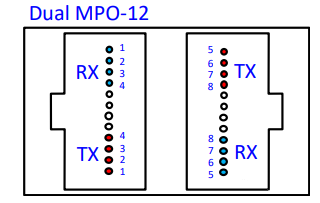
This solution uses a VCSEL (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser) with a wavelength of 850nm, a single-channel rate of 100Gbps PAM4, and requires 16 fibers. This can be seen as an upgraded version of 400G SR4 with double the channels. Its optical interface is MPO-16 or a two-row MPO-12, as shown in the diagram below.
2) 800G SR4.2
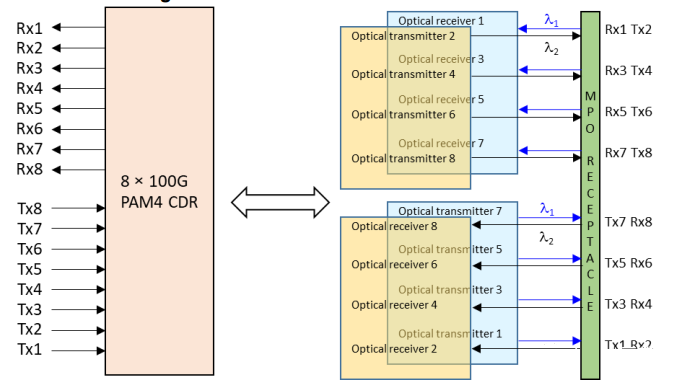
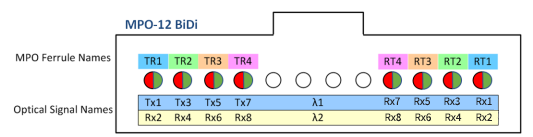
This solution uses two wavelengths, 850nm and 910nm, transmitting bidirectional signals in a single fiber, also known as bi-directional transmission. The module uses a DeMux to separate the two wavelengths. Each channel has a rate of 100Gbps PAM4, requiring 8 fibers, which saves half the fiber count compared to SR8.
Its block diagram and optical interface using MPO-12 are shown below.
For single-mode scenarios, multiple 800G optical module standards exist:
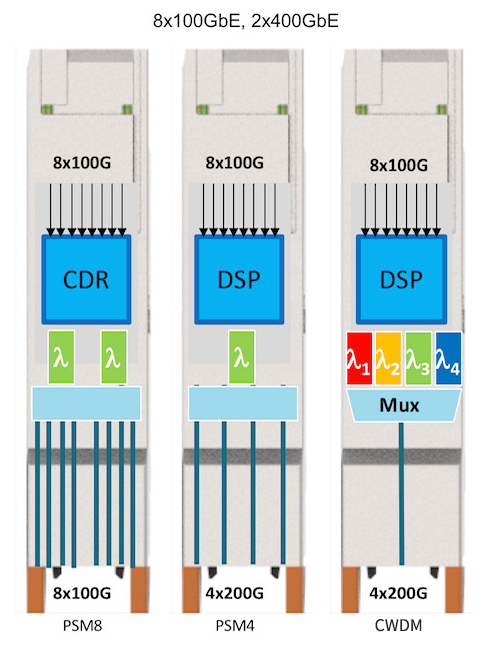
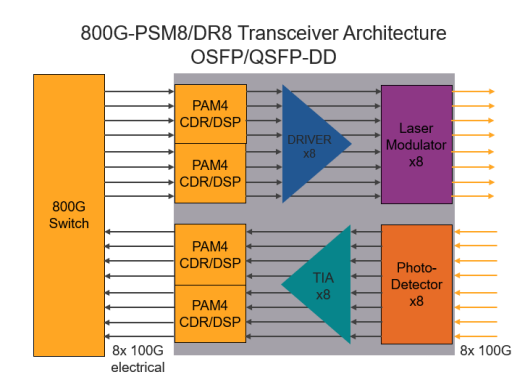
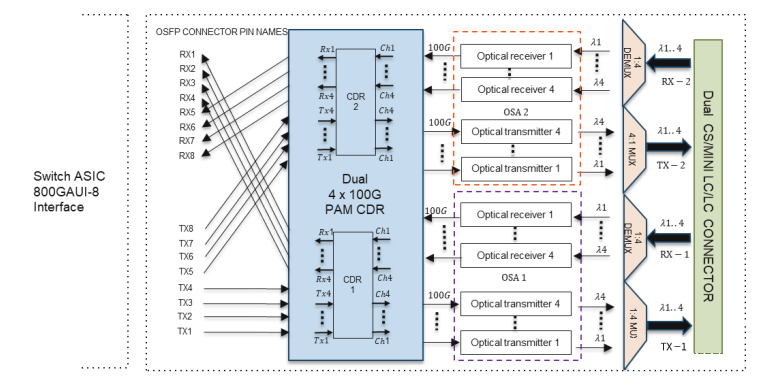
1) 800G DR8, 800G 2xDR4, and 800G PSM8
These three standards have similar internal architectures, including 8 Tx and 8 Rx, with each channel having a rate of 100Gbps, requiring 16 fibers.
- PSM8: Transmission distance of 100m.
- DR8 and 2xDR4: Corresponding to a transmission distance of 500m. The optical interface of 2xDR4 is 2 MPO-12, allowing interconnection with 400G DR4 optical modules for convenient data center upgrades. PSM8 and DR8 use MPO-16 optical interfaces.
2) 800G 2xFR4 and 2xLR4
These standards have similar internal structures, containing 4 wavelengths, each with a rate of 100Gbps. Using Mux reduces the fiber count, requiring 4 fibers, as shown in the diagram below.
- Both are upgrades from the 400G FR4 and LR4 optical modules, using CWDM4 wavelengths (1271/1291/1311/1331nm).
- 2xFR4: Supports a transmission distance of 2km.
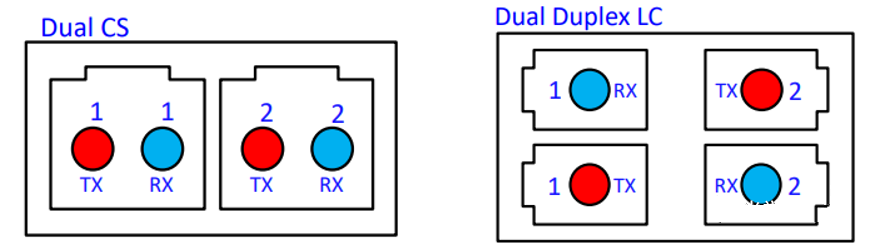
- 2xLR4: Supports a transmission distance of 10km. The optical interface uses dual CS or dual duplex LC.
3) 800G FR4
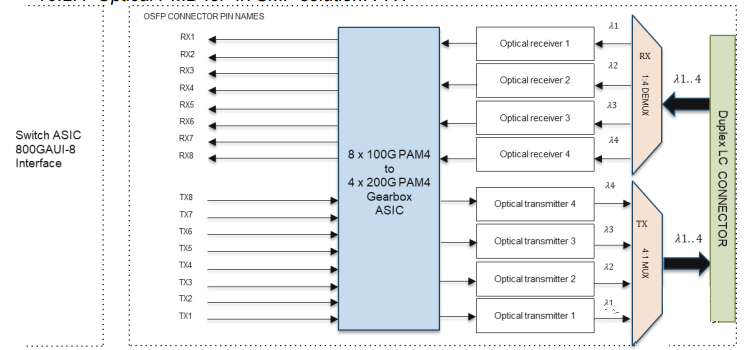
This solution uses four wavelengths, each with a rate of 200Gbps, requiring two fibers and supporting a transmission distance of 2km, as shown in the diagram below.
- Uses a duplex LC optical interface.
4) 800G FR8
This solution uses eight wavelengths, each with a rate of 100Gbps, requiring two fibers and supporting a transmission distance of 2km, as shown in the diagram below. The eight wavelength channels are 1271/1291/1311/1331/1351/1371/1391/1411nm.
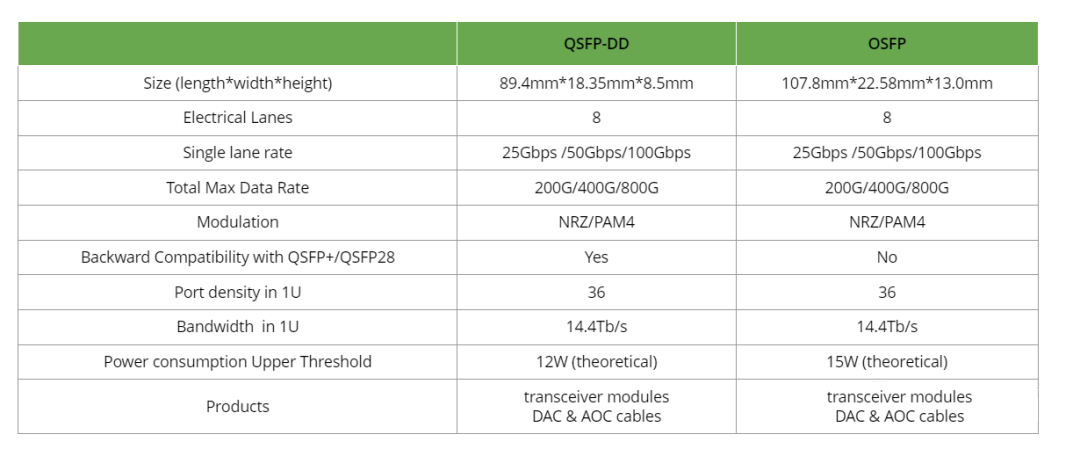
Both QSFP-DD and OSFP can support 800G, with their comparison illustrated below. The QSFP-DD800 has made some supplementary updates for 800G optical modules.
Main Differences:
- Size: OSFP is slightly larger.
- Power Consumption: OSFP has a slightly higher power consumption than QSFP-DD.
- Compatibility: QSFP-DD is fully compatible with QSFP28 and QSFP+, whereas OSFP is not compatible.
Currently, mass-produced single-mode 800G optical modules mainly use the EML (Electro-absorption Modulated Laser) solution. Whether silicon photonics can gain a foothold remains uncertain, primarily depending on cost and power consumption. For single-wave 200G solutions, EML or thin-film lithium niobate are two possible technological routes.