Fiber optic cables and Ethernet cables are two of the most important data transmission cable standards available, but because their use cases often overlap and colloquialisms mean that each name is sometimes used interchangeably, it’s important to know the differences between fiber optic cables and Ethernet cables. One is typically used for industrial applications or where extremely long cable runs are required, while the other is designed for home networks, small offices, and connecting consumer devices.
There are different types of both, with different features and designed for different uses, so a simple comparison between fiber and Ethernet cables isn’t the whole story. Here’s everything you need to know about fiber and Ethernet cables to help you decide which is right for your network.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Ethernet Cables?
First of all, let us clear up a common misconception. You will find many guides on the web that state that copper cables are Ethernet cables and that fiber cables are a separate type. While this is not entirely incorrect, the fact is that both fiber and copper are actually two different types of Ethernet cable.
This means that both types of Ethernet cables are designed to transmit data in LAN and WAN networks using Ethernet technology but through different media. Fibre optic cables transmit data in the form of light, while copper Ethernet cables use low-voltage electricity to do the same job.
In short, Ethernet cables are a group of cables used in local area networks and wide area networks for data communications. In addition to fiber optic cables and twisted pair cables, coaxial cables are also a type of Ethernet cable.
Types of Ethernet Cable
Contrary to popular belief that twisted-pair copper cables are the only Ethernet cables, the following are the three types of Ethernet cables.
- Twisted pair cables
- Fibre optic cables
- Coaxial cables
What are Fiber Optic Cables?
Fibre optic cables are a type of Ethernet cable known for their unparalleled speed of data transmission. You may be interested to know that fiber optic cables connect the world via the Internet. Fibre optic cables run deep under the oceans around the world, connecting entire continents and countries via the Internet.
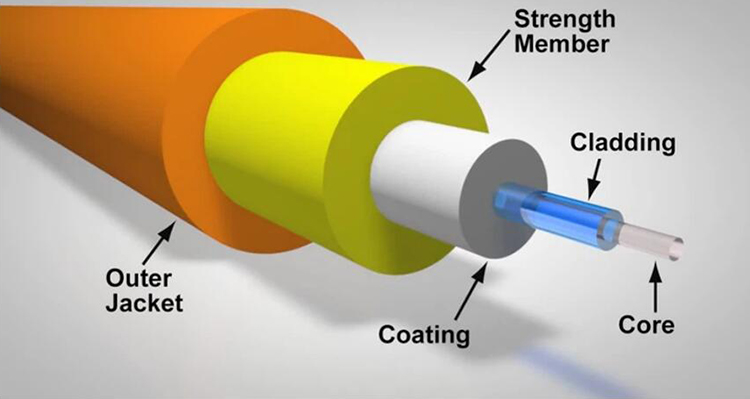
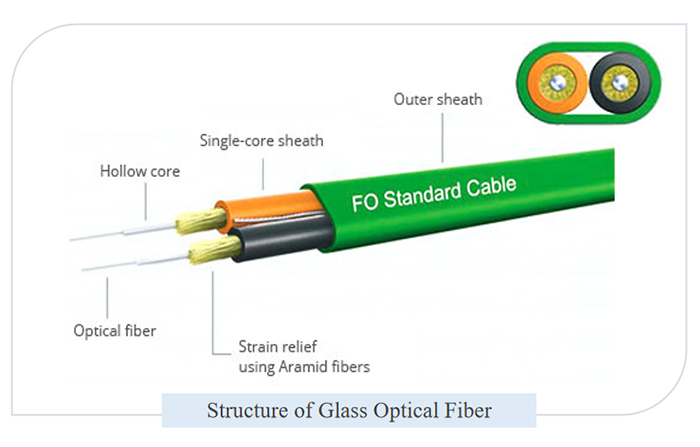
The actual fiber inside these cables, which carries data as a beam of light, is thinner than a human hair. But it allows data to be transmitted at speeds that no other data transmission medium can match.
Types of Fiber Optic Cable
There are two types of fiber optic cable. Single-mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fiber can only carry a single beam of light and is used for long distance transmission. They have less insertion loss, which is the resistance in the cable, and are therefore more efficient. If you are reading this article on the internet, which you probably are, single mode fiber is responsible for making it possible.
The second type of fiber is multi-mode fiber. This type of fiber has a comparatively thicker core that can carry multiple beams of light simultaneously. The downside is that it has more insertion loss, which means the signal loses integrity over long distances.
Multi-mode fiber is therefore best used in data centers, server rooms, etc. where transmission distances are short.
Fiber Optic Cable vs. Ethernet Cable: Knowing the Difference
The biggest difference between the two types of cable is obviously their construction and the way they transmit data. But there is more. Check out the list below to find out what else makes the two types of networks different.
- Fiber optic cables have a smaller diameter than their twisted pair counterparts.
- Fiber optic Ethernet cables are most commonly used for long distance transmission. Twisted-pair Ethernet cables are used for both long and short distances.
- Twisted pair copper cables come in a wide variety of options to choose from, but fiber cables come in only two types: single-mode fiber cables and multi-mode fiber cables.
- Fibre cables are more fragile than twisted pair cables, which are quite durable to withstand physical impact.
- Copper Ethernet cables are quite fast, and even Cat6 and Cat6a cables support Gigabit and 10 Gigabit speeds, but are not as fast as fibre optic cables.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Fiber Optic Cables
Let’s start with the disadvantages. The main disadvantage of using fiber optic cables is that they are too fragile. All fibre optic cables have a limited bend angle and bending them beyond this can cause damage. Fibre optic cables are also more expensive.
However, the advantages of these cables are obviously faster data transfer speeds and better signal integrity. Because fiber optic cables use a beam of light to carry data, they are not subject to electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference is a major problem with twisted pair cables.
In short, fragility and higher cost are the disadvantages, and faster speeds and overall better performance are the advantages of using fiber optic cables.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Twisted-pair Ethernet Cable
Twisted-pair Ethernet cables also have their fair share of advantages and disadvantages. The main advantage of using these cables is that they are very cost-effective and offer excellent speed. The key is to choose the right cable for the right application and you will never need fibre. More on this later.
If twisted pair cables are unshielded, they’re more likely to suffer from interference, resulting in higher latency.
How to Choose the Right Cable?
Choosing between fiber optic and Ethernet cables is easier than you might think. If you are setting up a home network, a small office network, or just want to run a few network cables over any distance up to 100 meters, Ethernet cables will be the simplest, cheapest, and most straightforward solution. Assess how much shielding and what kind of data rate you need and buy the appropriate category of cable. The RJ45 connector is fairly ubiquitous, especially in consumer equipment, so you’ll find it easier to set up, run, and source than a powerful fiber-optic alternative.
However, due to the limitations of Ethernet cabling, fiber is always an alternative. If you want to offer better guarantees for the integrity of your data, if you need to run cables over a particularly long distance, or if you are building on top of an existing fiber optic network, then fiber optic cables will be the better solution.
As with Ethernet cables, when choosing fiber optic cables, be sure to select the type of single-mode or multi-mode cable that is best suited to the role you have in mind. Don’t buy more powerful or shielded cables than you need, as these will just end up costing you extra money unnecessarily.