Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 800G Optical Modules
As of this year, 800G optical modules have entered mass production, driven by the increasing demand from the rise of AI technologies like ChatGPT. Understanding the classifications and characteristics of these modules is crucial for optimizing network performance.
Classification of 800G Optical Modules
800G optical modules can be categorized into two main types based on single-channel rates: 100G per channel and 200G per channel. The simpler 100G per channel modules can be implemented more quickly, while the 200G per channel modules require more advanced optical components and often involve gearboxes for signal conversion due to the current maximum electrical interface rate of 112Gbps PAM4.
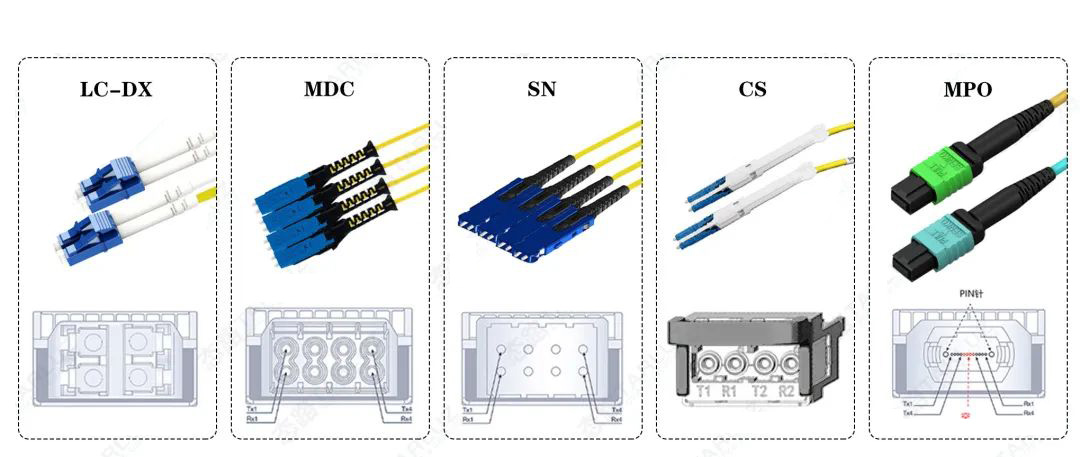
Types of 800G QSFP-DD Optical Ports
The main types of optical ports for 800G QSFP-DD optical modules are duplex LC connectors, VSFF connectors (including SN, CS, and MDC), and MPO connectors (MPO-12 and MPO-16).
Multimode 800G Optical Module Standards
- 800G SR8: Uses a VCSEL solution at 850nm with a single-channel rate of 100Gbps PAM4, requiring 16 fibers and featuring an MPO-16 or dual MPO-12 optical interface.
- 800G SR4.2: Uses two wavelengths (850nm and 910nm) for bi-directional transmission over 8 fibers, reducing fiber count by half compared to SR8 and using an MPO-12 interface.
Single-mode 800G Optical Module Standards
- 800G DR8, 2xDR4, and PSM8: Require 16 fibers with a single-channel rate of 100Gbps. DR8 and 2xDR4 support up to 500m, while PSM8 supports up to 100m. DR8 and PSM8 use an MPO-16 interface, while 2xDR4 uses dual MPO-12 interfaces for compatibility with 400G DR4 modules.
- 800G 2xFR4 and 2xLR4: Utilize four wavelengths with a single-channel rate of 100Gbps, requiring four fibers. 2xFR4 supports up to 2km, and 2xLR4 supports up to 10km, both using dual CS or dual duplex LC interfaces.
- 800G FR4: Uses four wavelengths with a 200Gbps single-channel rate over two fibers, supporting up to 2km and using a duplex LC interface.800G FR8: Uses eight wavelengths with a 100Gbps single-channel rate over two fibers, supporting up to 2km, with wavelengths ranging from 1271nm to 1411nm.
Differences Between QSFP-DD and OSFP
QSFP-DD and OSFP modules both support 800G. However, they differ in size, power consumption, and compatibility:
- Size: OSFP modules are slightly larger.
- Power Consumption: OSFP modules typically consume more power.
- Compatibility: QSFP-DD modules are fully compatible with QSFP28 and QSFP+ modules, while OSFP modules are not.
Choosing the Right Patch Cord for QSFP-DD800G Optical Modules
Key Considerations
- Transmission Mode: Select single-mode or multimode fiber patch cords (OM3, OM4, or OM5) based on the optical module’s transmission mode.
- Polarity: Ensure correct polarity to connect the transmitter and receiver ends correctly. The TIA standard defines three types of polarity for MPO patch cords: Type A, Type B, and Type C.
- Connector Gender: MPO connectors have male connectors with alignment pins and female connectors without. Ensure one connector is male and the other is female for proper alignment.
- Link Loss: Ensure the link loss falls within the power budget to maintain proper link function.
Summary
800G QSFP-DD optical modules represent a significant advancement in network technology, offering high-speed data transmission over various distances using single-mode or multimode fibers. Choosing the right fiber optic patch cord involves considering the transmission mode, polarity, connector gender, and link loss. Understanding these factors ensures optimal performance and compatibility within your network infrastructure, making 800G QSFP-DD modules a valuable solution for high-bandwidth requirements.