From start-ups to large enterprises, data centers are ever-increasingly important to the IT infrastructure of companies of all sizes. The growth of data centers is mainly due to the surge in cyber security threats and the growing need for companies to have robust infrastructure.
DAC and AOC are two types of cables commonly used in data centers today. Knowing the difference between DAC and AOC cables can help IT managers make an informed choice. DAC cables and AOC cables are available in a variety of configurations to suit network requirements. Each cable is available in 10G SFP+, 25G SFP28, 40G QSFP+, and 100G QSFP28 data rates, with expansion options from 40G to 4x10G or 100G to 4x25G variants. This blog will explain the different DAC and AOC cable types, identify the proper cable, and choose the right cable.
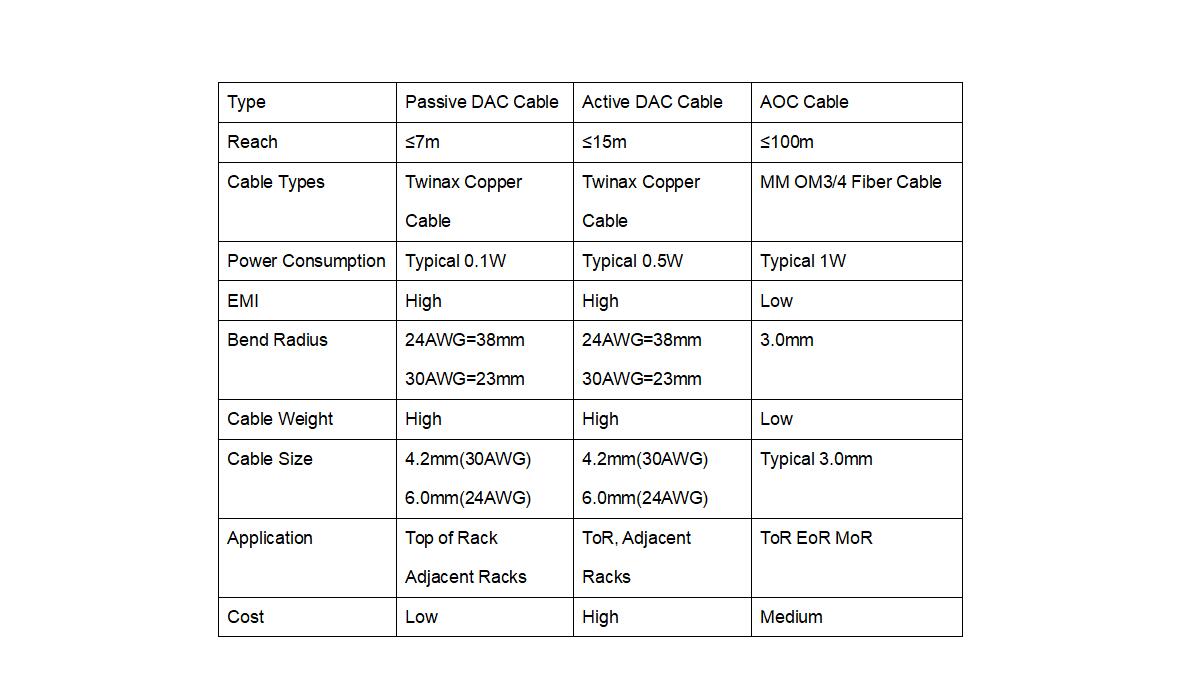
DAC Cables and AOC Cables
The data center network is a network like no other. Every component must meet the most demanding technical specifications. This makes it costly. If you want to find a way to control costs, you must know how to optimize every cable in the system. One step toward optimization is knowing the difference between DAC and AOC cables.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the DAC Cable?
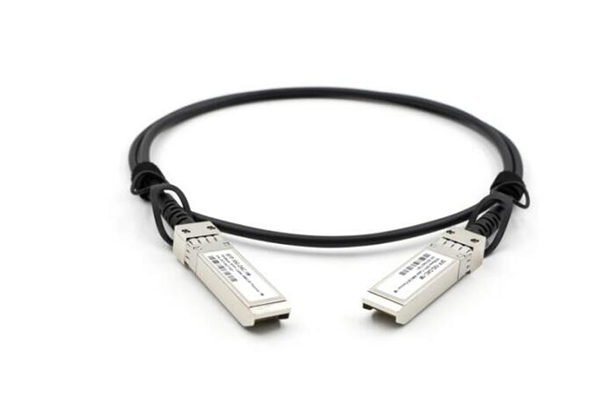
The direct attach cable (DAC) is a copper cable with connectors on both ends. Connectors often have a latch or other device that prevents accidental loosening of the connection. DAC cables are designed for intra-rack interconnection of equipment that is not normally rack-mounted. These devices include network switches, servers, and storage devices. DAC cables are called direct-attach cables because they connect directly to the device used for interconnection. They are also known as “Twinax” cables because they consist of two twisted pairs of copper wires and are commonly referred to as “Twinax” cables.
What Types of DAC Cables Are There?
There are two types of direct connect cables: passive DAC and active DAC. Passive DAC cables transmit data without signal conditioning. These cables are less expensive than active DAC cables. Active DAC cables contain electronics that amplify the signal. This signal is constantly compared with the data being sent and any changes are detected and corrected. Active DAC cables are much more expensive, but the improved signal helps applications such as long distances and high-resolution audio.
Depending on data rate and connector type, DAC cables typically come in the following configurations: 10G SFP+ DAC cable, 25G SFP28 DAC cable, 40G QSFP+ DAC cable, 56G QSFP+ DAC cable, 100G QSFP28 DAC cable, 200G QSFP56 DAC cable, 400G QSFP-DD DAC Cable, 40G DAC Breakout Cable, 56G DAC Breakout Cable, 100G DAC Breakout Cable, 200G DAC Breakout Cable, 400G DAC Breakout Cable.
What is the AOC Cable?
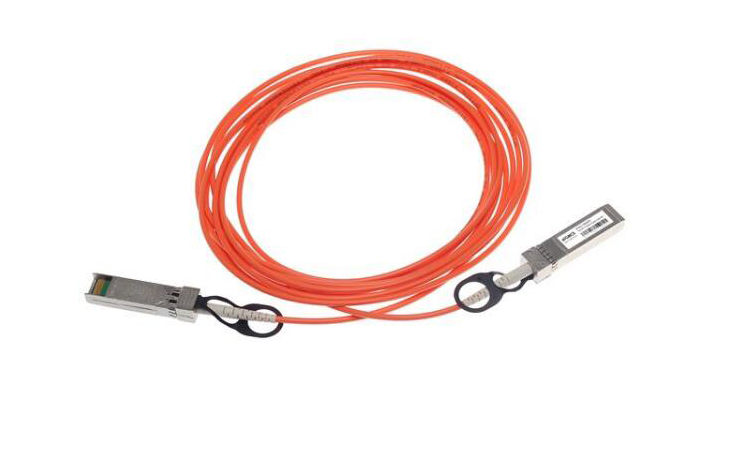
Active Optical Cables (AOCs) are multimode fiber optic cables with SFP connectors on both ends. This design requires an external power source to drive the signal, which is why “active” appears in the name. Signals do not pass passively through fiber optic lines.
The most common application for AOC cables is in data centers. They can efficiently connect switches, servers, and storage devices in different racks in the same center. Its operating lengths are typically within 100 meters and speeds of up to 400G are achievable at these distances.
At 100 meters, AOC cables tend to shine when compared to their cost-to-capacity ratio.
What Types of AOC Cables Are There?
Depending on the data rate and connector type, AOC cables typically come in the following configurations: 10G SFP+ AOC cable, 25G SFP28 AOC cable, 40G QSFP+ AOC cable, 56G QSFP+ AOC cable, 100G QSFP28 AOC cable, 200G QSFP56 AOC cable, 400G QSFP-DD AOC Cable, 40G AOC Breakout Cable, 56G AOC Breakout Cable, 100G AOC Breakout Cable, 200G AOC Breakout Cable, 400G AOC Breakout Cable.
DAC vs. AOC Cables, What’s the Difference?
Choosing the right cables is critical to building a data center that performs well while keeping costs down. While the choice is not always straightforward, considering a few factors can fully determine what to use and how.
Power Consumption
Generally, AOC cables have a higher power consumption than DAC cables, 1-2w. While the power consumption of DAC active cables is less than 1w, the power consumption of passive cables is almost zero, less than 0.15w, due to the heat dissipation design of direct connection copper cables. Therefore, the operating expense in terms of power consumption will be lower when using the DAC option.
Transmission Distance
Using fiber optic technology, the AOC cable has a transmission distance of up to 100 meters, while the link length of the DAC cable is limited to 10 meters (passive DAC: 7 meters; active DAC: 10 meters). In summary, DAC cabling solutions are suitable for short-distance transmission, while AOC solutions are suitable for long-distance networking.
NOTE: The maximum distance a signal can be transmitted through the DAC cable depends on the data transfer rate. The link length decreases as the data transfer rate increases, for example, a 100G DAC cable can only travel up to 5 meters.
Cost
Roughly speaking, the internals of a DAC are relatively simple, with fewer components, and copper cables are much cheaper than fiber optic cables. When implemented in a large data center, extensive use of DAC cables will save a lot of money over AOC solutions. For short-range applications, DACs do offer a cost-effective solution over AOCs, but for long-range applications, it is wise to make an overall cost list by comparing the two solutions.
Anti-electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) refers to disturbances generated by external sources that affect electrical circuits. As discussed earlier, active optical cables contain optical fibers – a dielectric that does not conduct electrical current. So, AOC fiber optic cable can be used in most cases, because AOC fiber optic cable is not subject to electromagnetic interference. However, direct-attach copper cables are susceptible to electromagnetic interference due to the property of copper to send electrical signals. Therefore, the environment of use is very important to avoid adverse reactions, performance degradation, or complete system failure.
How to Choose DAC and AOC Cables?
Based on the comparison above, I think you already recognize the difference between DAC cables and AOC cables. Average data centers can benefit from the high-performance networking of DACs and AOCs. Both the DAC and AOC are compact, all-in-one network connectivity solutions. But how to choose DAC and AOC cables?
Another consideration is routing flexibility. DACs are made of thick copper cables whose thickness increases with bandwidth. 100G DACs are thicker than 10G DACs. However, the thickness of the AOC optical cable is fixed and has nothing to do with the bandwidth. AOC fiber optic cables (3.0mm diameter) are typically twice as thick as normal copper wire (approximately 6.0mm). In tight spaces, AOCs are easier to install than DACs.
DACs are widely used in high-performance computer systems, large-scale commercial operations, and storage applications, and are ideal for short-distance transmission. The DAC consumes very little power, is extremely cost-effective, and offers excellent performance. They are ideal for connecting rack-mounted network servers and storage devices to top-of-rack switches.
Active optical cables are ideal for long-distance transmission because they can transmit data up to 100 meters, have ultra-high bandwidth, small size, and flexibility, resistance to electrical interference, and easy installation.