Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules are crucial components in network setups, but like any tech, they can encounter issues. Learn about the common problems with SFP modules, signs of failure, and how to address them effectively in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding SFP Modules and Their Potential Issues
Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules are integral to modern networking, enabling the connection of various network devices and enhancing communication efficiency. However, despite their reliability, SFP modules can sometimes fail or perform suboptimally. In this first part, we’ll explore the common reasons why SFP modules go bad and how you can identify these issues.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is an SFP Module?
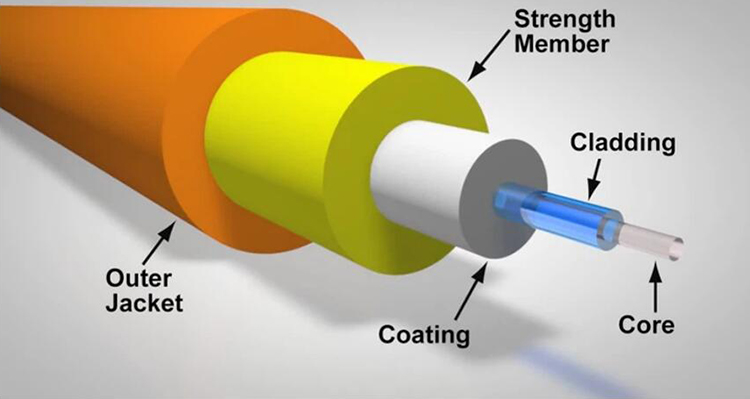
SFP modules are compact, hot-swappable transceivers used to interface network devices like switches, routers, and servers. They support various types of network connections, including Ethernet, fiber, and serial. Each SFP module contains a transmitter and a receiver, converting electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa.
Common Causes of SFP Failure
Physical Damage: One of the most straightforward reasons for SFP module failure is physical damage. Dropping the module or exposing it to extreme temperatures can cause internal components to malfunction. Inspect the module for visible signs of damage like cracks or bent pins.
Wear and Tear: Over time, the pins and connectors of an SFP module can wear out. Frequent insertion and removal of the module can lead to mechanical wear, affecting its performance. Regularly check and clean the connectors to ensure a stable connection.
Compatibility Issues: Using an incompatible SFP module can lead to problems. Ensure that the SFP module is compatible with your network hardware and matches the required specifications. Mismatched wavelengths or data rates can cause connectivity issues or prevent the module from working altogether.
Environmental Factors: SFP modules are sensitive to environmental conditions. Excessive dust, humidity, or temperature variations can affect their performance. Installing modules in a controlled environment and keeping them clean can mitigate these risks.
Electrical Failures: Internal electrical failures can also cause SFP modules to malfunction. Issues like short circuits or power surges can damage the delicate circuitry inside the module. Using surge protectors and ensuring stable power supplies can help prevent electrical problems.
Signs of SFP Module Failure
Recognizing when an SFP module is failing is crucial for maintaining network performance. Here are some common signs to watch for:
Loss of Connectivity: If the network connection suddenly drops or becomes unreliable, the SFP module might be the culprit. Check the connection status and run diagnostic tests to determine if the module is functioning correctly.
Error Messages: Many network devices will display error messages or alerts if an SFP module is faulty. Pay attention to any warnings or logs from your network equipment, as these can provide clues about the issue.
Inconsistent Performance: If you notice fluctuations in network performance, such as slow speeds or packet loss, it could indicate a problem with the SFP module. Perform performance tests to assess if the module is contributing to the issue.
Troubleshooting and Testing SFP Modules
Before replacing an SFP module, it’s essential to troubleshoot and test it thoroughly:
Swap and Test: If you suspect an SFP module is failing, try swapping it with a known good module. This can help you determine if the problem lies with the module itself or with other parts of the network.
Check Compatibility: Verify that the SFP module is compatible with your network devices. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and documentation to ensure proper matching.
Inspect for Damage: Examine the module and its connectors for any signs of physical damage or wear. Clean the connectors gently with a dry, lint-free cloth if needed.
Update Firmware: Ensure that your network devices have the latest firmware updates, as outdated software can sometimes cause compatibility issues with SFP modules.
Solutions and Best Practices for SFP Modules
In the second part, we’ll delve into effective solutions for dealing with problematic SFP modules and best practices to extend their lifespan and maintain optimal performance.
Replacing Faulty SFP Modules
When an SFP module is confirmed to be faulty, replacing it is often the best solution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth replacement process:
Power Down: Before removing the faulty SFP module, power down the network device to avoid potential damage or data loss.
Remove the Faulty Module: Gently release and remove the problematic SFP module from its slot. Handle it carefully to avoid damaging the connectors.
Install the New Module: Insert the new SFP module into the slot, ensuring it is securely seated. Avoid forcing it into place, as this can cause damage.
Power Up and Test: Turn the network device back on and test the new SFP module. Check for proper connectivity and performance to confirm that the replacement has resolved the issue.
Best Practices for Maintaining SFP Modules
Adhering to best practices can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of SFP modules:
Keep Modules Clean: Dust and debris can affect the functionality of SFP modules. Regularly clean the modules and their slots to ensure a stable connection. Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove dust without damaging the components.
Monitor Environmental Conditions: Maintain a controlled environment for your network equipment. Ensure that the temperature, humidity, and dust levels are within recommended ranges to prevent SFP module degradation.
Use Proper Handling Techniques: Handle SFP modules with care. Avoid touching the connectors with bare hands and ensure they are properly seated in their slots. Use antistatic bags for storage and transportation to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect SFP modules for signs of wear or damage. Conduct routine performance tests to identify potential issues before they affect network operations.
Stay Informed About Firmware Updates: Keep your network devices updated with the latest firmware. Manufacturers often release updates that can improve compatibility and performance with SFP modules.
Purchase Quality Modules: Invest in high-quality SFP modules from reputable manufacturers. While cheaper alternatives might be available, they may not meet the same standards of reliability and performance.
Conclusion
SFP modules are vital components of modern networking infrastructure, but like all technology, they can experience issues. Understanding the common causes of SFP module failure and recognizing the signs of trouble can help you address problems efficiently. By following best practices for maintenance and troubleshooting, you can extend the life of your SFP modules and ensure your network remains robust and reliable. If you encounter persistent issues, consulting with a network specialist or the module manufacturer can provide additional support and solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q:Can 1G SFP work with 10G SFP
A:Yes, technically, a 1G SFP can physically fit into a 10G SFP port, but it will not work as intended. The mismatch in data rates will likely result in communication errors, link instability, and degraded network performance. Mixing different SFP speeds can lead to potential issues such as data packet loss, increased latency, and network congestion.
To address these issues when mixing 1G and 10G SFPs, it is recommended to use media converters or rate-selectable SFP modules that can adapt to different speeds. These devices can help bridge the gap between different SFP speeds and ensure compatibility within the network.
From a current perspective, with the advancement of technology and the widespread adoption of higher network speeds, it is becoming increasingly important to maintain uniformity in SFP speeds to optimize network performance and reliability. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid mixing 1G and 10G SFPs whenever possible to prevent potential compatibility issues and ensure seamless network operation.
Q:Do Walsun appliances support direct attach cable (DAC)?
A:Yes, Walsun appliances support a passive DAC in release 10.5 and later.
Q:Which port must I insert the DAC into?
A:DAC is inserted into the 10G port on the appliance.
Q:Does the 1G port support a DAC?
A:No. The DAC might fit into a 1G port but is not supported.
Q:How can I order a DAC?
A:Contact your Walsun sales representative to order a DAC.
Q:Can I mix DAC and fiber transceivers on the same appliance?
A:Yes. You can mix DAC and fiber transceivers on the same appliance. Each 10G port supports both options.
Q:Can I mix SFP+ fiber and DAC in ports that are part of the same link aggregation channel?
A:No. There must be symmetry between all elements in the same link aggregation channel.
Q:Which transceivers use the MPO type connector?
A:Only 40G QSFP+ SR4 transceiver and 100G QSFP28 SR4 transceivers use the MPO type connector. All other fiber transceivers use the LC type connector.
Q:Are special adapters required for 25G, 50G, and 100G ports?
A 100G port can support five speeds: 10G, 25G, 40G, 50G, and 100G. 1G speed is not supported on the 100G port. 50G and 100G ports use the same transceiver. The appliance determines the speed, and not the port.
Only 50G/100G (QSFP28) and 40G (QSFP+) transceivers can be directly used on a QSFP28 interface. Use a QSA28 adapter on a QSFP28 interface to use 10G (SFP+) and 25G (SFP28) transceivers.
Related Article:
Can SFP 10G LR Modules Support 1G Unlocking the Potential of Your Network
Can SFP Be Hot Plugged Understanding the Flexibility of Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules
Can You Use a 10G SFP in a 1G Port_ Understanding Compatibility and Best Practices
Can a 25G DAC Run at 10G Exploring the Versatility of Modern Network Cables
How to Determine if Your Cable is SFP or Experiencing Failure