Fibre optic cables are available in a variety of types, each designed to cater to the specific requirements of diverse applications. These cables can be tailored with additional features to suit their intended purpose, whether used for armored, aerial, or indoor distribution. For every location, installers must meticulously assess cable placement to satisfy specific demands.
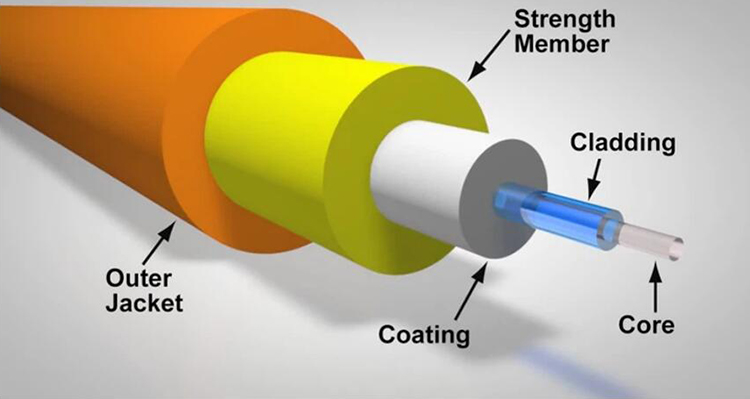
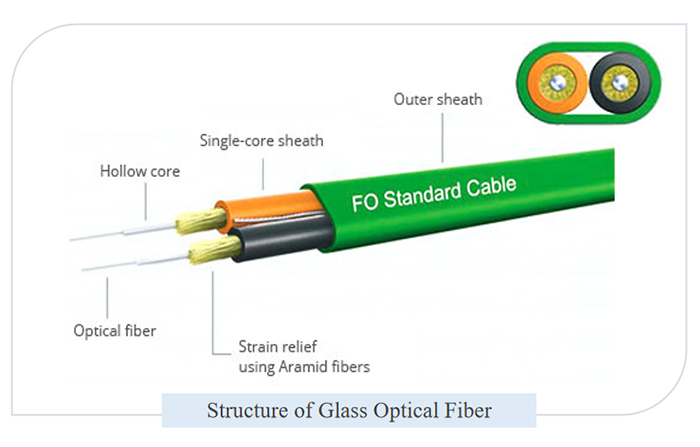
As the fiber optic cable is liable to break, a protective jacket is necessary to safeguard the conductors and shielding inside. The cable jacket serves as the initial protection layer against moisture, mechanical damage, flames, and chemicals, thus being key in maintaining a secure and efficient fiber optic network.
Comprehending the dissimilarities between jackets, identifying the significance of fire ratings, and sticking to correct protocols are fundamental to preserving the integrity and safety of the network. By ensuring the use of cables with the correct fire ratings, the integrity and reliability of the network can be maintained.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy is the Jacket of the Fiber Optic Cable So Important?
Fibre optic cables typically comprise fiber cores, coatings, strength members, and outer jackets. The outer jacket acts as a safeguarding layer for the cable, offering resistance against fire and moisture.
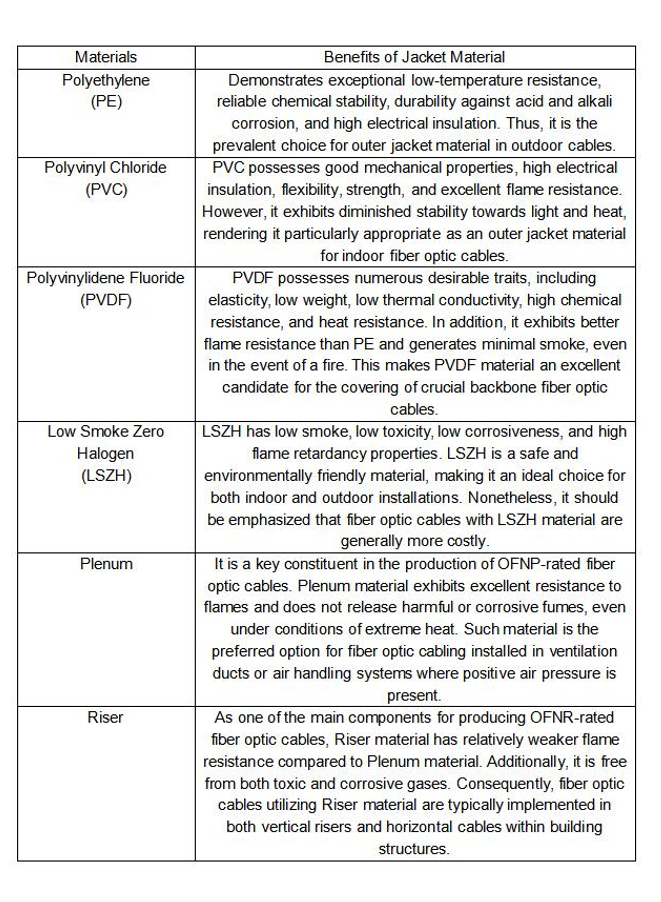
The effectiveness of the outer jacket is crucial in the case of a fire outbreak in a data center. Fibre optic cable jackets are available in various materials, each with its own unique properties (including varying resistance to fire) and designated application scenarios. Common exterior jacket materials comprise PE, PVC, PVDF, LSZH, Plenum, and Riser. The following table portrays their performance and applicable environments.
Fiber Optic Cable Fire Rating
In the National Electrical Code (NEC), fiber optic cables are categorized into various fire ratings, including OFNP/OFCP, OFNR/OFCR, OFNG/OFCG, and OFN/OFC.
OFNP/OFCP is the highest flame-retardant rating in the NEC standards, meaning it is plenum-grade. If a fan forces airflow onto a bundle of such cables, the flames will self-extinguish within five metres, without any resultant toxic or corrosive gases being emitted.
OFNR/OFCR is classified as vertical riser-rated and is ranked second. If a fan is used to direct forced airflow onto a bundle of riser-rated fiber optic cables, the flames will self-extinguish within 5 meters. There are no requirements for smoke or toxicity.
OFNG/OFCG and OFN/OFC are classified as commercial-grade and general-purpose-grade, respectively. Fiber optic cables adhering to these standards are commonly used in environments with reduced fire resistance requirements.
OFNP vs. OFNR
As noted, OFNP and OFNR are two types of optical fiber cables used in buildings. OFNP cables have fire-resistant and low-smoke characteristics, with the highest fire rating among fiber cables, rendering them irreplaceable. These cables are consequently predominantly positioned in plenum areas. Conversely, OFNR cables exhibit less impressive fire resistance and low-smoke features than OFNP cables. OFNP plenum cables constitute feasible substitutes for OFNR cables. It is noteworthy that OFNP cables can be used in riser areas while OFNR fiber optic cables are not suitable for use in plenum spaces. Both OFNP and OFNR can be used in general-purpose areas.
What Fire Rating Can be Achieved with Different Outer Jacket Materials?
Although the fire rating of fiber optic cables is not determined by the outer jacket material directly, Plenum usage as the outer jacket material can generally result in the attainment of an OFNP fire rating for the fiber optic cable during NEC flame retardant testing. The usage of PVC or Riser as the outer jacket material can achieve an OFNR fire rating. The OFN fire rating can be achieved by the use of LSZH as the outer jacket material.
In brief, fiber optic cables with outer jackets composed of Plenum, PVC/Riser, or LSZH materials are able to fulfill the fire resistance criteria of data centers.
How to Select the Fiber Optic Cable Outer Jacket Materials Based on the Layout Area?
Plenum material is suitable for horizontal cabling areas and areas with inflatable environments such as conduits and air handling systems. In these environments, where air circulation is present and fire incidents are difficult to control, using OFNP-rated flame-retardant fiber optic cables is the best choice.
Riser/PVC material is suitable for vertical backbone cabling areas, providing connectivity between entrance equipment or computer rooms and different floor telecommunication closets. The likelihood of large-scale fires is low in these areas, and achieving an OFNR fire rating is sufficient.
LSZH material is commonly used in general-purpose areas. Even in the event of a fire, LSZH cables release non-toxic smoke, thereby avoiding harm to rescue personnel.