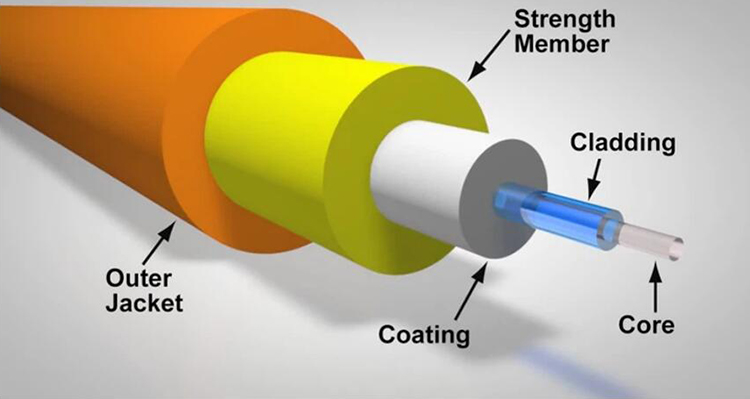
In recent years, major changes have taken place in the field of telecommunications. Fiber optics are steadily replacing copper wires as the proper means of signal transmission and have the unique advantage of transmitting high-speed data over long distances. Various optical devices are credited to this communication development, with fiber optic cables leading the way. Widely used in telecommunications and computer networks. Optical fibers are flexible, transparent fibers drawn from glass (silicon dioxide) or plastic into diameters slightly thicker than human hair. Plastic optical fiber vs. glass optical fiber: Which is preferable?
Table of Contents
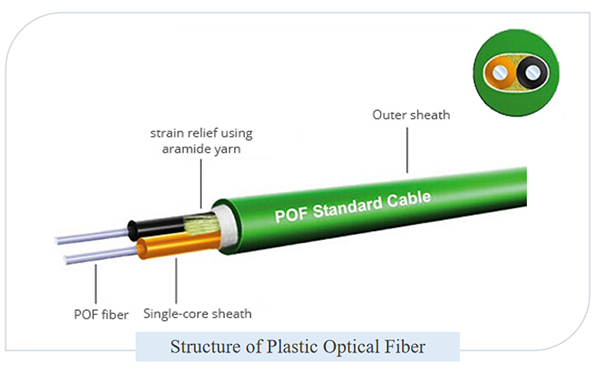
ToggleWhat is Plastic Optical Fiber?
Plastic Optical Fiber (Polymer Optical Fiber or POF), is an optical fiber made of plastic. Typically consists of acrylic (PMMA) as the core (96% of the fiber cross-section, 1 mm diameter) to aid in light transmission and a fluorinated polymer as the cladding material. Plastic fibers use harmless green or red light that is easily visible to the naked eye. Plastic fibers are safe to install around the home and pose no risk to curious children. But today, high-performance plastic fibers based on perfluorinated polymers are more used.
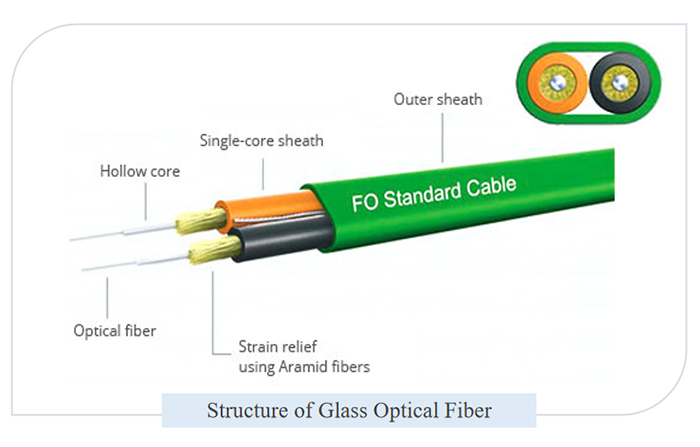
What is Glass Optical Fiber?
Glass optical fibers consist of a pure glass (SiO 2 ) core and a less pure glass or plastic cladding. As a fragile fiber, it cannot be cut, spliced, or repaired, and it is less flexible and less resistant to accidental breakage. Glass fiber optic cables are extremely versatile and robust, and are available in a variety of configurations, end fittings, and adapter types. Ideal for harsh environments, it functions even when subjected to mechanical stress, high temperatures, or chemicals.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Optical Fiber
Pros:
(1) Low cost of constituent materials and less complicated manufacture of POF, and installation cost of related components is also not high.
(2) Flexible, strong and capable of bending farther without cracking or breaking.
(3) The network using plastic optical fiber can be handled and installed by untrained personnel or home users.
(4) It is safe to install in the house, and the plastic optical fiber uses harmless green or red light that is easy to see with the naked eye.
Cons:
(1) Due to the signal attenuation and dispersion of POF is usually very high, only for short distances.
(2) POF cannot withstand extreme temperatures like glass optical fibers and is prone to degradation/yellowing over time.
These characteristics of plastic fiber make it the first choice for more lighting and decorative applications. Due to the flexibility and vibration resistance of plastic fibers, they are also well-suited for automotive and industrial lighting applications. Although the narrow spectrum of transmitted light is listed as a disadvantage, it is actually an advantage for medical instruments. Plastic optical fibers are often used to illuminate the interior of the body during surgery because certain wavelengths other than visible light are harmful and cannot exist. Listed as our Industrial Control Plastic Optical Fiber:
Pros and Cons of Glass Optical Fiber
Pros:
(1) It can be used in high-temperature places such as furnaces, ovens, and condensers in large engines, and can also be used in extremely low-temperature areas such as cold storage.
(2) Glass optical fiber can be used for long sensing distances because the glass core can transmit a wider spectrum and fast transmission speed.
(3) Ability to use photoelectric sensors in areas where photoelectric sensors cannot normally be used. With this advantage, sensors with various housings, mounting styles and functions can be selected for specific applications.
(4) Glass fiber optic cables are thin and light, so they are optimized for tight spaces and small targets.
Cons:
(1) Installation requires well-trained technicians, and the tools and equipment for fiber termination are usually expensive.
(2) The core diameter of the glass fiber is very small, so the technical requirements for coupling light into the core area (such as the light source) are relatively high.
(3) Glass optical fiber is fragile and is more likely to break if it is not handled properly.
The main applications of glass fibers are communication, sensors and measurement systems. High transmission rates and low dissipation factors make them ideal for long-distance, high-speed communication applications. They are also ideal if used in corrosive environments or extreme temperatures.
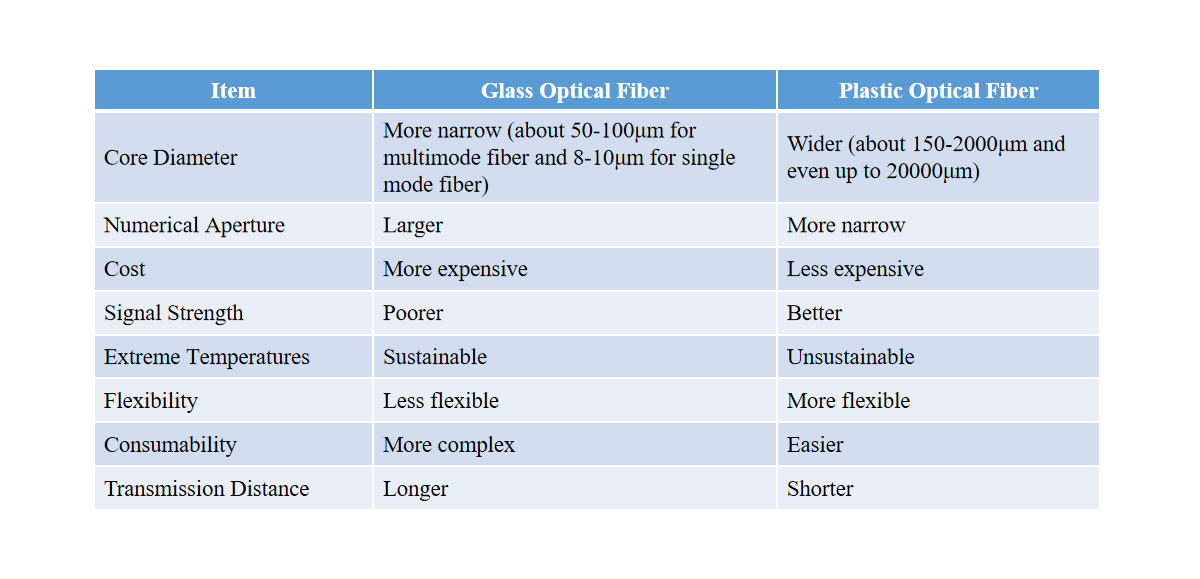
Plastic Optical Fiber vs. Glass Optical Fiber
One of the main differences is the composition of the wire: Glass optical fibers are made of pure glass, while plastic optical fibers are made of plastic polymers. The difference in composition affects some properties of the two types of fiber.
An important difference is resistance: Plastic optical fibers are more durable because glass is a more sensitive and less resistive material than plastic. So it is more suitable for use in bellows and domestic installations, where the fiber is more prone to breakage.
(1) Physical Properties
Plastic optical fiber components are simpler, cheaper, and have greater flexibility and resistance to bending, shock, and vibration. In addition, it is lighter in weight than glass fiber optics. Plastic optical fibers require no special tools or techniques to handle and require no training in operation or installation. Just cut it with scissors, plug it in and that’s it. This is what makes plastic optical fiber a low-cost alternative to glass fiber or copper at medium distances and bit rates of 10 Gbps.
Glass fibers require more difficult and delicate handling and the tools and equipment for fiber termination are often expensive. While being well mechanically protected, glass optical fibers have a higher information transmission capacity and lower loss. Moreover, glass optical fibers are optimized for small spaces and small targets. They can be used with both visible red and infrared light and are compatible with a long list of fiber heads.
(2) Applications
Plastic optical fibers are commonly used for low-speed, short-distance (up to 100 meters) applications in digital home appliances, home networks, industrial networks, and car networks. It plays an important role in the data transmission of military communication networks and multimedia equipment.
Glass fiber optic cables can be applied for longer-distance transmission at higher speeds in office networks. What’s more, they are adept to hostile conditions, and more durable than their plastic counterparts.