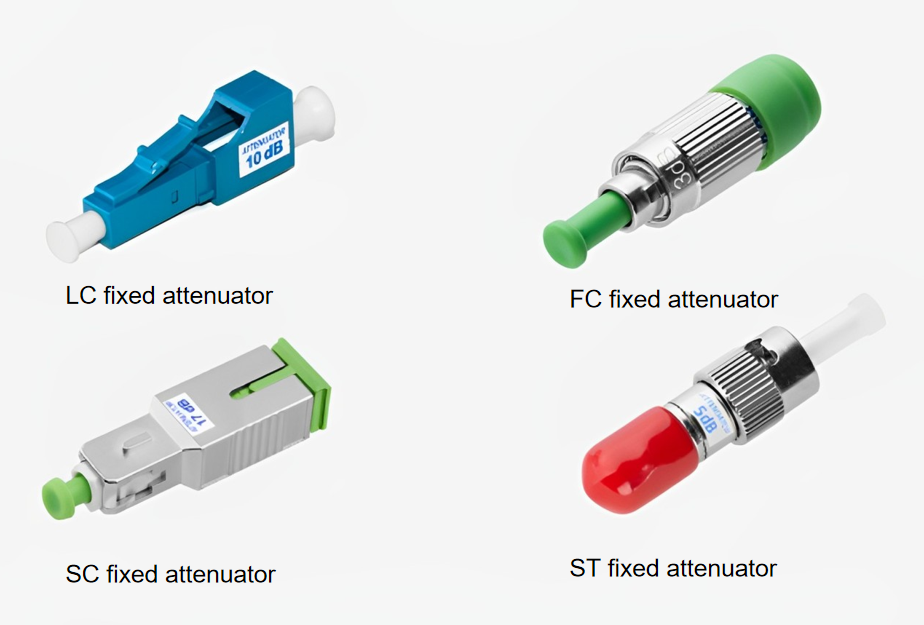
As we all know, too much and too little optical power can cause equipment errors. Excessive power can saturate the receiving amplifier, while insufficient power can interfere with the signal and cause noise problems. An optical fiber attenuator is an optical device used to attenuate the input power, preventing distortion of the optical receiver due to excessive power.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are Fiber Optic Attenuators?
Fiber optic attenuators are passive devices that reduce the strength of signals traveling through fiber optic cables. They introduce a controlled amount of signal loss into the pathway without significantly altering other signal characteristics, such as wavelength or phase. These attenuators are crucial in applications where fine-tuning or enhancing signal quality is important, including long-distance communication systems, fiber optic networks, and scientific testing setups.
How Many Types of Fiber Optic Attenuators are There?
Fixed Optical Attenuator
Fixed attenuator, as the name implies, is designed to provide a constant level of attenuation in optical fiber, typically ranging from 1dB to 30dB, such as 1dB, 5dB, or 10dB. Fixed optical attenuators may operate based on various principles. Preferred types often use doped fibers, misaligned splices, or total power loss, while less preferred types might use gap loss or reflective principles.
Fixed optical attenuators have various types, such as pigtail and converter types, and can be made with interfaces like FC, SC, ST, LC, MU, and others, making them convenient for daily cabling use. Typically, a single optical attenuator has two interfaces, male and female, which can be male-female or female-female. The male connector interface is generally used to plug into the device’s receiver or an adapter on an adapter panel, while the female connector interface is used to connect a fiber jumper. These attenuators are widely used in applications including telecommunication networks, optical fiber test facilities, Local Area Networks (LAN), and CATV systems.
Optical Variable Attenuator
An optical variable attenuator (OVA), or variable optical attenuator (VOA), typically employs a variable neutral density filter. VOAs are generally used for testing and measurement purposes, but they are also widely used in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) to equalize light power across different channels. VOAs are advantageous because they are stable, wavelength-insensitive, mode-insensitive, and offer a large dynamic range.
There are essentially two types of optical variable attenuators: stepwise variable attenuators and continuously variable attenuators. Stepwise variable attenuators adjust signal attenuation in defined increments, such as 0.1dB, 0.5dB, or 1dB. Continuously variable optical attenuators, on the other hand, allow for precise attenuation adjustment through flexible tuning. This enables operators to quickly and accurately adjust the attenuation level as needed without interrupting the circuit.
Single Mode and Multimode Fiber Optic Attenuator
Fiber optic attenuators can be used with two types of fiber cables: single mode and multimode. Therefore, optical attenuators are classified into single mode and multimode types. Typically, fiber optic attenuators are used in single mode long-haul applications, making the single mode type the most commonly used. However, multimode fiber optic attenuators are also available for use with multimode fiber cables. When selecting an optical attenuator, it is important to consider the attenuation range and the wavelength to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
What is the Role of Attenuation in Fiber Optics?
Attenuation, the decrease in signal strength as light travels through an optical fiber cable, significantly impacts the efficiency and reliability of communication systems. It can be caused by absorption, scattering, and bending losses.
Absorption Losses: Absorption losses occur when impurities or defects in the fiber material absorb the signal. Common sources include water molecules, metallic impurities, and additives introduced during manufacturing. These losses vary with wavelength and differ among types of optical fibers, with lower-loss fibers preferred for long-distance transmission applications.
Scattering Losses: Scattering losses are due to imperfections or irregularities in the fiber material. Rayleigh scattering, the primary form of scattering in fibers, happens when light interacts with tiny fluctuations in the refractive index along the fiber core. These losses increase with shorter wavelengths and can significantly contribute to overall attenuation, especially in high-capacity transmission systems.
Bending Losses: Bending losses occur when optical signals pass through bends or curves in the fiber optic cable. Light traveling along a curved path may escape through the cladding, resulting in signal loss. Factors such as the curvature radius, fiber diameter, and material characteristics affect bending losses. Minimizing these losses is crucial to maintaining signal quality and reducing attenuation in optical fiber systems.
Total Attenuation: The total attenuation experienced by a signal is a combination of absorption, scattering, and bending losses over the fiber’s length. Fiber optic attenuators are used to manage these losses by introducing controlled levels of attenuation to enhance signal quality and integrity. Attenuators are essential in managing attenuation effects, enabling effective optical communication over long distances and various network setups.
Applications of Fiber Optic Attenuators
The versatility of fiber optic attenuators makes them indispensable in various optical communication applications:
Long-Haul Transmission: In long-distance optical transmission systems, signal attenuation due to fiber optic losses or dispersion can degrade signal quality and limit transmission distances. Fiber optic attenuators are used to mitigate signal loss, thereby maintaining signal integrity and allowing for extended reach in optical networks.
Network Testing and Calibration: Fiber optic attenuators play a crucial role in network testing and calibration, allowing engineers to simulate different signal attenuation scenarios and evaluate network performance under realistic conditions. Precise control over signal levels afforded by attenuators enables accurate measurements and facilitates troubleshooting within optical networks.
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) Deployments: In FTTH deployments, where optical signals traverse varying distances between central offices and end-user premises, maintaining consistent signal levels is essential for reliable service delivery. Fiber optic attenuators allow service providers to optimize signal strength and reduce signal distortion, ensuring seamless connectivity for end-users.
Optical Amplifier Optimization: Optical amplifiers are commonly used to boost signal power in optical communication systems, particularly in long-haul transmission networks.
Uncontrolled high signal power can induce nonlinear effects, causing signal distortion. Fiber optic attenuators optimize amplifier performance by reducing excess signal power to within the amplifier’s linear operating range, maximizing signal quality and minimizing distortion.
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) Systems: DWDM systems enable the simultaneous transmission of multiple optical signals over a single fiber optic cable, significantly increasing network capacity. However, signal attenuation and dispersion can vary across different wavelengths, leading to channel imbalances and signal degradation. Fiber optic attenuators help equalize signal levels across DWDM channels, ensuring uniform performance and maximizing network efficiency. By balancing the signal power among different wavelengths, attenuators maintain the integrity and quality of the transmitted signals, which is crucial for the optimal performance of DWDM systems.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Attenuators
Integrating fiber optic attenuators into optical communication systems offers several key benefits:
Signal Optimization: Fiber optic attenuators, through precise control of signal strength, ensure optimal signal quality and integrity.This minimizes signal distortion and enhances overall network performance, ensuring clearer and more reliable communication.
Flexibility and Versatility: Fiber optic attenuators come in a wide range of attenuation options and form factors, providing flexibility to adapt to diverse application requirements and environmental conditions. This versatility allows them to be used in various scenarios, from long-haul transmission to local network adjustments.
Signal Stability: Attenuators play a crucial role in ensuring stable optical signals by counteracting fluctuations in optical power levels.This ensures consistent performance across different network segments and operating conditions, maintaining a steady and reliable signal flow.
Network Reliability:By mitigating signal distortion and maintaining signal quality, fiber optic attenuators enhance the reliability and uptime of optical communication networks.This reduces service disruptions and downtime, leading to a more dependable network infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness: Implementing fiber optic attenuators can extend the operational lifespan of optical components and infrastructure. By reducing the risk of signal degradation and equipment damage, attenuators help achieve long-term cost savings for network operators and service providers.