In the rapidly evolving world of networking, ensuring seamless and efficient data transmission is paramount. One of the crucial components in this puzzle is the Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver. But with so many options available, a common question arises: “Can I use any SFP?” The answer is both yes and no, and understanding the nuances can make a significant difference in your network’s performance.
Understanding SFP Transceivers
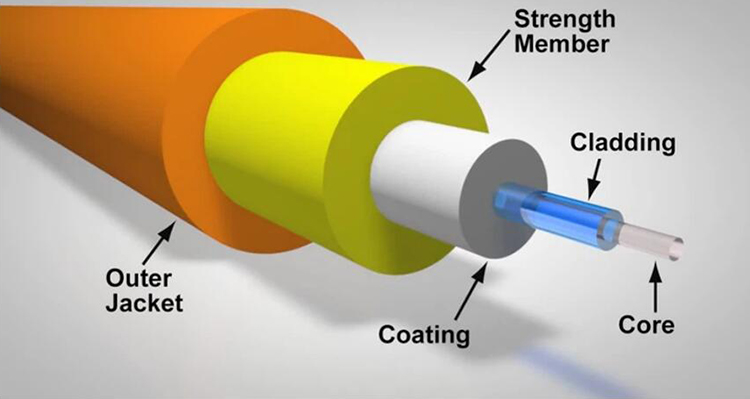
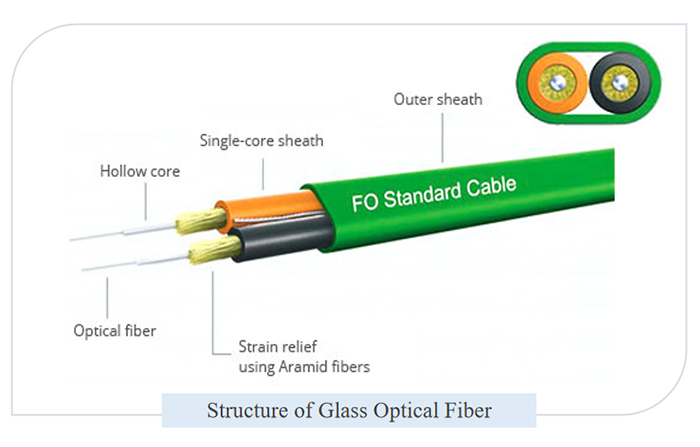
SFP transceivers are compact, hot-swappable devices used to connect switches and routers to fiber optic or copper networks. These versatile modules are essential for transmitting data over varying distances and mediums, making them indispensable in modern networking environments. However, not all SFPs are created equal, and choosing the wrong one can lead to compatibility issues, suboptimal performance, and even hardware damage.
Table of Contents
ToggleCompatibility: The Key Consideration
The primary factor to consider when selecting an SFP transceiver is compatibility. Different manufacturers often have proprietary specifications, and using an incompatible SFP can cause serious problems. Here are some critical aspects to keep in mind:
1. Vendor Lock-In
Many network equipment manufacturers (OEMs) implement vendor lock-in, restricting their devices to work only with their branded SFPs. While third-party SFPs might be more affordable, they can be blocked by the OEM firmware, leading to a non-functional network connection. It’s essential to check if your network equipment has such restrictions before purchasing SFPs.
2. Firmware and Software Compatibility
Even if an SFP physically fits into a port, firmware and software compatibility must be ensured. Network devices often require specific firmware versions to support certain SFP models. Incompatibility here can result in connectivity issues or degraded performance. Regularly updating your network device firmware can help maintain compatibility with newer SFP models.
3. Cable Type and Distance Requirements
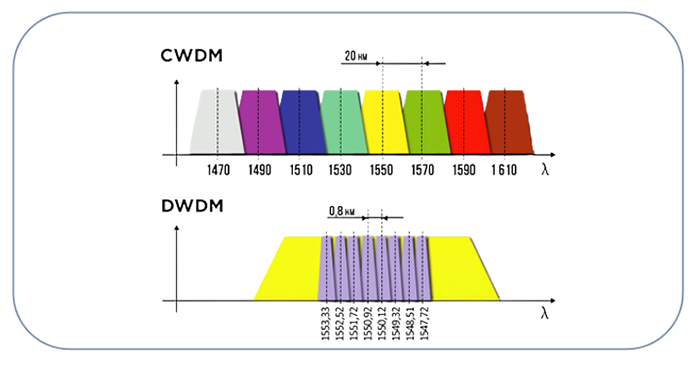
SFPs are designed to work with specific types of cables and over certain distances. For instance, an SFP designed for single-mode fiber (SMF) won’t work properly with multi-mode fiber (MMF). Additionally, the distance over which the SFP can transmit data (ranging from a few meters to several kilometers) is crucial for meeting your network needs. Ensure the SFP you choose matches the cable type and distance requirements of your setup.
Types of SFPs
SFP transceivers come in various types, each tailored for specific applications and network setups. Understanding these types can help you make an informed decision:
1. Standard SFP
Standard SFPs support data rates up to 1 Gbps and are suitable for general networking applications. They are commonly used in Ethernet switches, routers, and network interface cards (NICs).
2. SFP+
SFP+ transceivers support data rates up to 10 Gbps, making them ideal for high-performance networks. They are backward compatible with standard SFP ports but offer enhanced speed and performance.
3. SFP28
SFP28 transceivers support data rates up to 25 Gbps, catering to even higher performance needs. These are often used in data centers and environments requiring ultra-fast data transmission.
4. QSFP/QSFP+
Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) transceivers are designed for 40 Gbps data rates, while QSFP+ supports 100 Gbps. These are typically used in high-density data centers and enterprise networks.
5. BiDi SFP
Bidirectional (BiDi) SFP transceivers use a single fiber strand for both transmission and reception, effectively doubling the fiber capacity. They are an excellent choice for cost-effective network expansion without laying additional fiber.
The Importance of Quality
When selecting SFP transceivers, quality is paramount. High-quality SFPs ensure reliable and stable network performance, minimizing downtime and data loss. While third-party SFPs might offer cost savings, it’s essential to choose reputable brands that guarantee quality and compatibility. Inferior SFPs can lead to network instability, reduced lifespan of your equipment, and increased maintenance costs.
Ensuring Compatibility: Best Practices
Given the importance of compatibility, here are some best practices to follow when selecting and deploying SFP transceivers in your network:
1. Refer to Compatibility Lists
Most manufacturers provide compatibility lists for their network devices. These lists specify which SFP models are guaranteed to work with their equipment. Always refer to these lists before purchasing SFPs to ensure compatibility and avoid potential issues.
2. Test Before Deployment
Before deploying new SFPs across your entire network, test them in a controlled environment. This step can help identify any compatibility or performance issues before they impact your broader network. Testing ensures that the SFPs meet your network’s performance standards and are fully compatible with your existing equipment.
3. Monitor Network Performance
Regularly monitor your network’s performance after deploying new SFPs. Look for any signs of connectivity issues, data loss, or degraded performance. Early detection of issues allows for prompt resolution, minimizing any negative impact on your network operations.
4. Firmware Updates
Keep your network devices’ firmware up to date. Manufacturers frequently release firmware updates that enhance compatibility with newer SFP models and improve overall performance. Regular updates ensure that your network can take advantage of the latest advancements in SFP technology.
Exploring Cost-Effective Solutions
While OEM-branded SFPs ensure compatibility, they often come at a premium price. Third-party SFPs can be a cost-effective alternative, provided they are from reputable vendors and meet quality standards. Here’s how you can balance cost and quality:
1. Choose Reputable Vendors
If opting for third-party SFPs, select reputable vendors known for quality and reliability. Look for vendors who offer comprehensive testing and certification for their SFPs, ensuring they meet industry standards and are compatible with a wide range of network devices.
2. Read Reviews and Testimonials
Customer reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of third-party SFPs. Look for feedback from other network professionals who have used the same SFPs in similar environments to gauge their suitability for your needs.
3. Consider Warranties and Support
Choose vendors who offer warranties and technical support for their SFPs. A warranty provides peace of mind, ensuring that any faulty units can be replaced. Technical support can assist with troubleshooting and resolving any compatibility issues that may arise.
The Future of SFP Technology
As networking technology continues to evolve, so too will SFP transceivers. Emerging standards and advancements promise even higher data rates, greater efficiency, and improved compatibility. Staying informed about these trends can help you future-proof your network and take advantage of new capabilities.
1. Higher Data Rates
With the increasing demand for bandwidth, future SFPs are expected to support even higher data rates, potentially reaching 400 Gbps and beyond. These advancements will cater to the growing needs of data centers, cloud services, and high-performance computing environments.
2. Enhanced Power Efficiency
Future SFPs are likely to feature improved power efficiency, reducing the overall energy consumption of network devices. This trend aligns with the broader push towards green computing and sustainable IT practices.
3. Greater Compatibility
Efforts are ongoing to enhance compatibility across different vendors and network environments. Standardization initiatives aim to reduce vendor lock-in and ensure that SFPs can be seamlessly integrated into diverse networking setups.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right SFP transceiver is crucial for maintaining a reliable and high-performing network. While the question “Can I use any SFP?” may seem simple, the answer involves careful consideration of compatibility, quality, and future-proofing your network. By following best practices, exploring cost-effective options, and staying informed about technological advancements, you can ensure that your network operates at its best, now and in the future.
In conclusion, not all SFPs are interchangeable, but with the right knowledge and approach, you can select the perfect transceiver to meet your network’s needs, ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance.
Related Article:
SFP-CWGE27-80C 1.25G CWDM SFP 1270nm 80km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
TRENDnet TEG-MGBS10 Compatible 1000Base LX SFP 1310nm 10km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-GE35-2BX20 1000Base 2 Channels BX BIDI CSFP TX1310nm-RX1550nm 20km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-GE55-ZX 1000Base SFP ZX 1550nm 80km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-DWGE17-120C 1.25G DWDM SFP C17 100GHz 1563.86nm 120km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module