In the world of networking, understanding the various types of connectors and ports is crucial for ensuring seamless and efficient data transfer. One common question that arises is whether an RJ45 connector can be plugged into an SFP+ port. This query often stems from a desire to simplify network setups or upgrade existing infrastructure without a complete overhaul. To address this question, we must delve into the nature of these components and their compatibility.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are RJ45 and SFP+?
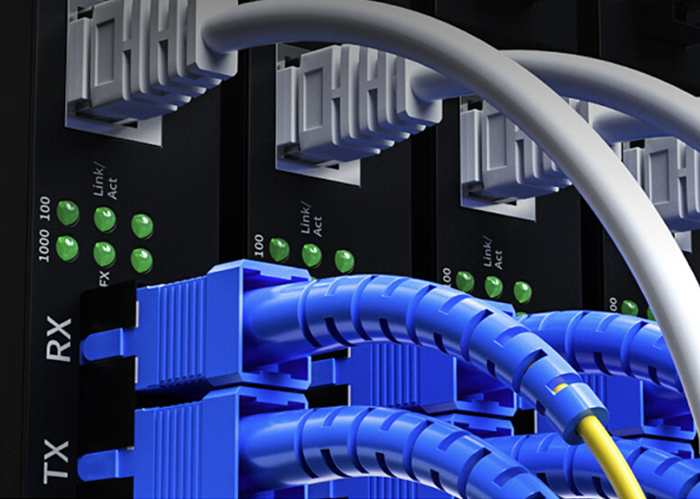
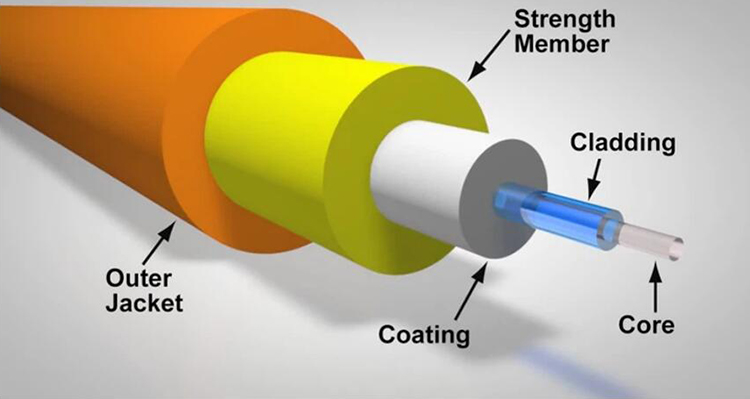
RJ45 connectors are ubiquitous in networking, used primarily for Ethernet connections. They are part of the twisted-pair cabling system and are typically associated with Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables, supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps over short distances. RJ45 connectors are widely recognized for their eight-pin modular connector format, which provides reliable and cost-effective solutions for local area networks (LANs).
On the other hand, SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) ports are designed for high-speed network applications, supporting data rates up to 10 Gbps and beyond. SFP+ modules are commonly used in data centers and enterprise environments where fiber optic or copper connections are needed to extend network reach and increase bandwidth. Unlike RJ45, SFP+ ports can accommodate various types of transceivers, including those for fiber optic cables and direct attach copper (DAC) cables.
The Compatibility Question
The direct answer to whether you can plug an RJ45 connector into an SFP+ port is no, you cannot directly connect an RJ45 connector to an SFP+ port. This is because they are fundamentally different in design and function. However, the situation is not as restrictive as it might seem. There are solutions available that bridge the gap between these two technologies.
SFP+ to RJ45 Transceivers
To facilitate the use of RJ45 connectors with SFP+ ports, manufacturers offer SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers. These transceivers convert the SFP+ interface to an RJ45 port, allowing you to use standard Ethernet cables with your SFP+ equipped devices. These transceivers are typically used in scenarios where upgrading to a fully fiber-based network infrastructure is not feasible or necessary.
Advantages of Using SFP+ to RJ45 Transceivers
- Cost-Effective Upgrades: For organizations looking to upgrade their network infrastructure incrementally, SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers offer a cost-effective solution. They allow the use of existing copper cabling, minimizing the need for extensive rewiring.
- Flexibility: These transceivers provide flexibility in network design, enabling a mix of fiber and copper connections. This is particularly beneficial in environments where certain segments of the network require higher speeds and longer distances covered by fiber, while others can function efficiently with copper.
- Ease of Use: Installing SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers is straightforward. They are hot-swappable, meaning they can be inserted or removed without powering down the device, reducing downtime and maintenance disruptions.
Considerations and Limitations
While SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers offer significant advantages, there are also considerations to keep in mind:
- Distance Limitations: Copper connections have distance limitations compared to fiber optics. For instance, Cat6a cables can support 10 Gbps up to 100 meters, whereas fiber optic cables can extend this range significantly.
- Power Consumption: SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers generally consume more power than fiber optic transceivers. This can be a critical factor in large-scale deployments where power efficiency is a priority.
- Latency: Although the impact is minimal, copper connections typically have slightly higher latency compared to fiber optics. In high-performance computing environments, even minor latency differences can be significant.
Conclusion
In summary, while you cannot directly plug an RJ45 connector into an SFP+ port, the use of SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers provides a practical solution. These transceivers enable the integration of RJ45-based infrastructure with modern SFP+ ports, offering a balance between performance, cost, and flexibility. In the next part, we will explore real-world applications and further technical details that highlight the benefits and limitations of using these transceivers in various networking scenarios.
Real-World Applications of SFP+ to RJ45 Transceivers
Understanding the practical applications of SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers helps in making informed decisions about network upgrades and expansions. These transceivers are particularly useful in various scenarios:
- Hybrid Network Environments: Many organizations operate hybrid networks that include both copper and fiber optic connections. SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers facilitate the seamless integration of these different mediums, allowing for a versatile and scalable network architecture.
- Data Centers: In data centers, where high-speed connections and minimal downtime are critical, SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers enable the use of existing copper cabling for short-distance connections while utilizing fiber optics for long-distance links. This approach helps in optimizing costs and maintaining high performance.
- Enterprise Networks: For enterprises with extensive legacy copper infrastructure, transitioning to fiber optics can be gradual. SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers enable this transition by allowing fiber optic switches and routers to connect with existing copper-based devices.
Technical Specifications and Performance
To ensure optimal performance when using SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers, it is essential to consider their technical specifications:
- Data Rate: Most SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers support 10GBASE-T, which provides 10 Gbps Ethernet over twisted-pair cabling. Some transceivers also support multi-rate operation, allowing them to work with 1000BASE-T (1 Gbps) and 100BASE-TX (100 Mbps) networks.
- Cable Type: These transceivers are compatible with Cat6a or higher cabling to ensure 10 Gbps performance. Using lower category cables can result in suboptimal performance and reduced distance capabilities.
- Operating Temperature: Given the varying environments in which these transceivers operate, they are designed to function within a broad temperature range. This is particularly important in data centers and industrial settings where temperature control can be a challenge.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation process for SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers is straightforward. They are designed to be plug-and-play, minimizing the need for complex configurations. However, some best practices should be followed:
- Compatibility Check: Ensure that the SFP+ port and the transceiver are compatible. While most SFP+ ports are standardized, checking for specific compatibility with the transceiver model can prevent issues.
- Firmware Updates: Keeping the network devices’ firmware up to date ensures that they can support the latest transceivers and features. Regular updates can also enhance security and performance.
Testing: After installation, performing thorough testing is crucial. This includes verifying the connection speed, checking for errors, and ensuring that the network performance meets the required standards.
Future-Proofing Your Network
As network demands continue to grow, future-proofing becomes a key consideration. SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers offer a bridge to future technologies while utilizing existing infrastructure. However, planning for the future involves more than just hardware:
- Scalability: Ensure that your network design can accommodate future expansions. This might involve planning for additional SFP+ ports or considering modular switch designs that can easily integrate new transceivers and technologies.
- Training: Network administrators should be trained in the latest technologies and best practices. This includes understanding how to effectively deploy and manage SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers and other networking components.
- Monitoring: Implementing robust network monitoring tools can provide insights into performance and potential issues. Proactive monitoring helps in maintaining optimal network health and quickly addressing any arising problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while an RJ45 connector cannot be directly plugged into an SFP+ port, the use of SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers provides a viable and efficient solution for integrating these technologies. By understanding the applications, technical specifications, and best practices for using these transceivers, organizations can make informed decisions that enhance their network infrastructure. Whether in data centers, enterprise networks, or hybrid environments, SFP+ to RJ45 transceivers play a crucial role in enabling high-speed, flexible, and cost-effective network connections.
As network technologies evolve, staying informed and adaptable ensures that your infrastructure can meet current demands and future growth, ultimately driving better performance and connectivity in a world increasingly reliant on robust and high-speed networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q:Can 1G SFP work with 10G SFP
A:Yes, technically, a 1G SFP can physically fit into a 10G SFP port, but it will not work as intended. The mismatch in data rates will likely result in communication errors, link instability, and degraded network performance. Mixing different SFP speeds can lead to potential issues such as data packet loss, increased latency, and network congestion.
To address these issues when mixing 1G and 10G SFPs, it is recommended to use media converters or rate-selectable SFP modules that can adapt to different speeds. These devices can help bridge the gap between different SFP speeds and ensure compatibility within the network.
From a current perspective, with the advancement of technology and the widespread adoption of higher network speeds, it is becoming increasingly important to maintain uniformity in SFP speeds to optimize network performance and reliability. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid mixing 1G and 10G SFPs whenever possible to prevent potential compatibility issues and ensure seamless network operation.
Q:Do Walsun appliances support direct attach cable (DAC)?
A:Yes, Walsun appliances support a passive DAC in release 10.5 and later.
Q:Which port must I insert the DAC into?
A:DAC is inserted into the 10G port on the appliance.
Q:Does the 1G port support a DAC?
A:No. The DAC might fit into a 1G port but is not supported.
Q:How can I order a DAC?
A:Contact your Walsun sales representative to order a DAC.
Q:Can I mix DAC and fiber transceivers on the same appliance?
A:Yes. You can mix DAC and fiber transceivers on the same appliance. Each 10G port supports both options.
Q:Can I mix SFP+ fiber and DAC in ports that are part of the same link aggregation channel?
A:No. There must be symmetry between all elements in the same link aggregation channel.
Q:Which transceivers use the MPO type connector?
A:Only 40G QSFP+ SR4 transceiver and 100G QSFP28 SR4 transceivers use the MPO type connector. All other fiber transceivers use the LC type connector.
Q:Are special adapters required for 25G, 50G, and 100G ports?
A 100G port can support five speeds: 10G, 25G, 40G, 50G, and 100G. 1G speed is not supported on the 100G port. 50G and 100G ports use the same transceiver. The appliance determines the speed, and not the port.
Only 50G/100G (QSFP28) and 40G (QSFP+) transceivers can be directly used on a QSFP28 interface. Use a QSA28 adapter on a QSFP28 interface to use 10G (SFP+) and 25G (SFP28) transceivers.
Related Article:
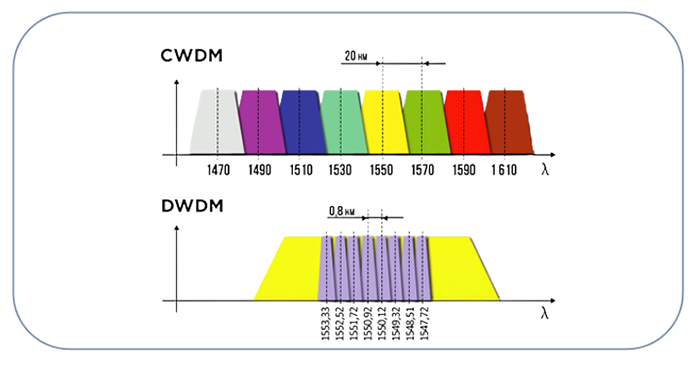
SFP-CWGE27-80C 1.25G CWDM SFP 1270nm 80km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
TRENDnet TEG-MGBS10 Compatible 1000Base LX SFP 1310nm 10km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-GE35-2BX20 1000Base 2 Channels BX BIDI CSFP TX1310nm-RX1550nm 20km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-GE55-ZX 1000Base SFP ZX 1550nm 80km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
SFP-DWGE17-120C 1.25G DWDM SFP C17 100GHz 1563.86nm 120km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module