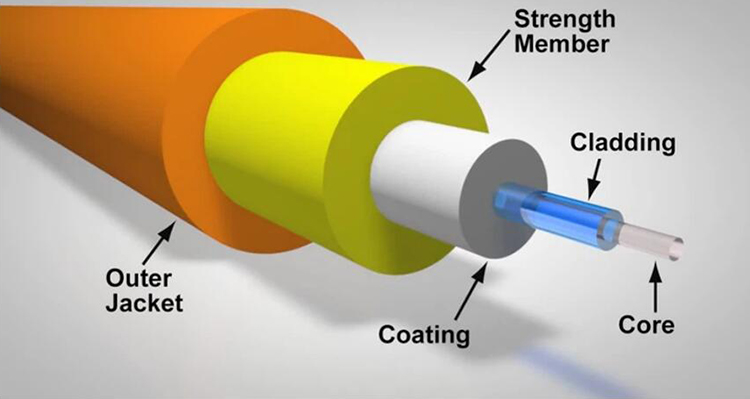
In the ever-evolving landscape of networking, ensuring robust and efficient data transmission is paramount. Two crucial components that play a significant role in this domain are the Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules and media converters. To begin our journey into connecting SFP to a media converter, it’s essential to understand what these devices are and why they are so pivotal.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an SFP Module?
An SFP, or Small Form-factor Pluggable module, is a compact, hot-swappable transceiver used for both telecommunication and data communications applications. Its primary function is to convert electrical signals into optical signals (or vice versa), facilitating high-speed data transmission over long distances. SFP modules are versatile, supporting a range of standards including Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and SONET/SDH.
What is a Media Converter?
A media converter, on the other hand, is a device that bridges different media types. In the context of networking, it typically converts signals from copper-based Ethernet to fiber optics and vice versa. This conversion is crucial for extending network distances beyond the limits of copper cabling and for integrating newer fiber-based infrastructure with existing copper networks.
Why Connect SFP to a Media Converter?
Connecting an SFP module to a media converter opens up a world of possibilities in terms of network flexibility and scalability. Here are some compelling reasons why this connection is beneficial:
- Extended Reach: Fiber optics, facilitated by SFP modules, allow data transmission over much greater distances compared to traditional copper cables. By using a media converter, you can extend the reach of your network without a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure.
- Enhanced Speed and Bandwidth: SFP modules support higher bandwidths and faster data transfer rates, which are essential for modern applications that demand rapid and reliable connectivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Upgrading an entire network to fiber optics can be prohibitively expensive. Media converters offer a cost-effective solution by enabling gradual upgrades and integration with current systems.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Media converters provide the flexibility to mix and match different types of media and network protocols, making it easier to scale your network as needs evolve.
The Process of Connecting SFP to Media Converter
Connecting an SFP module to a media converter is a straightforward process, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure optimal performance. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Choose the Right Components
First and foremost, ensure that the SFP module and media converter you select are compatible with each other and with your network requirements. This involves checking specifications such as data rate, wavelength, and connector type.
Step 2: Insert the SFP Module
Carefully insert the SFP module into the SFP slot on the media converter. SFP modules are designed to be hot-swappable, meaning you can insert them without powering down the device. Ensure the module is securely seated to avoid connection issues.
Step 3: Connect the Fiber Optic Cable
Next, connect the appropriate fiber optic cable to the SFP module. The type of fiber cable (single-mode or multi-mode) should match the specifications of the SFP module. Secure the connection by gently pushing the cable into the SFP module until it clicks into place.
Step 4: Connect the Copper Ethernet Cable
On the other side of the media converter, connect the copper Ethernet cable. This cable will link the media converter to your existing network equipment, such as a switch or router.
Step 5: Power Up and Test
Once all connections are made, power up the media converter. Most media converters have LED indicators to show the status of the connections. Verify that these indicators signal a successful connection. Conduct a thorough test by transmitting data across the link to ensure everything is functioning as expected.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly integrate an SFP module with a media converter, enhancing your network’s capabilities and performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While connecting an SFP to a media converter is generally straightforward, you might encounter some common issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
No Signal Detection
If the media converter does not detect a signal from the SFP module, ensure that the SFP module is fully inserted and the fiber optic cable is properly connected. Check the compatibility of the SFP module with the media converter and verify that both devices are functioning correctly.
Slow Data Transmission
If you experience slow data transmission, confirm that the SFP module and media converter support the required data rates. Additionally, check for any issues with the fiber optic cable, such as bends or breaks, which could impair signal quality.
Intermittent Connectivity
Intermittent connectivity issues can be caused by loose connections or incompatible components. Recheck all connections and ensure that the SFP module, media converter, and fiber optic cable are all compatible and securely connected.
Advantages of SFP and Media Converter Integration
Integrating SFP modules with media converters not only solves immediate connectivity challenges but also brings a host of advantages that future-proof your network infrastructure:
Improved Network Reliability
Fiber optic connections, facilitated by SFP modules, are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference compared to copper cables. This results in a more stable and reliable network, especially in environments with high levels of electrical noise.
Scalability
As your network grows, the flexibility offered by media converters allows you to incrementally upgrade parts of your network to fiber optics. This scalable approach ensures that your infrastructure can adapt to increasing demands without requiring a complete overhaul.
Energy Efficiency
Fiber optic cables consume less power than copper cables for long-distance transmissions. By integrating SFP modules with media converters, you can reduce the overall power consumption of your network, contributing to a greener and more cost-efficient operation.
Real-World Applications
The integration of SFP modules and media converters is prevalent across various industries, each benefiting from the enhanced connectivity and performance:
Enterprise Networks
Large corporations often have sprawling campus networks that require high-speed, long-distance data transmission. By using SFP modules and media converters, enterprises can ensure robust inter-building connectivity, supporting applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and large-scale data transfers.
Telecommunications
Telecom providers rely heavily on fiber optics to deliver high-speed internet and communication services to their customers. Media converters with SFP modules enable these providers to extend their networks efficiently and economically.
Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, reliable and fast data transmission is critical for automation and control systems. The rugged environments of factories and plants necessitate the use of fiber optics, which are more durable and resistant to harsh conditions compared to copper cables. Media converters facilitate this integration, ensuring seamless operation of industrial networks.
Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities demand high-speed, secure data transmission for applications such as medical imaging, electronic health records, and telemedicine. The combination of SFP modules and media converters ensures that these critical systems operate efficiently and reliably.
Future Trends
The landscape of networking is continually evolving, and the integration of SFP modules with media converters is poised to play a pivotal role in future developments. Some trends to watch for include:
Higher Data Rates
As data consumption continues to surge, there will be a growing demand for SFP modules and media converters that support higher data rates, enabling even faster and more efficient networks.
Increased Adoption of Single-Mode Fiber
Single-mode fiber, which supports longer distances and higher bandwidths than multi-mode fiber, is becoming more prevalent. Future media converters will likely be optimized to support this trend, offering even greater connectivity options.
Smart Networks
The rise of smart technologies and IoT (Internet of Things) will drive the need for more sophisticated network infrastructure. Media converters integrated with SFP modules will be essential in creating flexible, adaptive networks capable of supporting a myriad of smart devices and applications.
In conclusion, connecting an SFP module to a media converter is a powerful way to enhance your network’s performance and extend its capabilities. By understanding the components, following proper installation steps, and leveraging the advantages of this integration, you can build a future-proof network that meets the demands of today and tomorrow. Whether in enterprise, telecom, industrial, or healthcare settings, the synergy between SFP modules and media converters will continue to drive innovation and connectivity in the digital age.