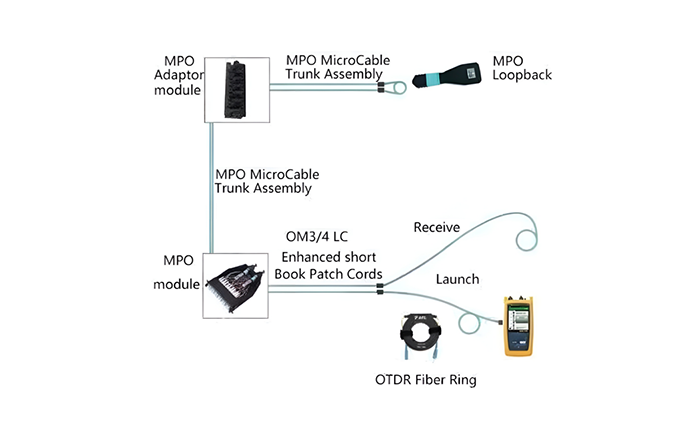
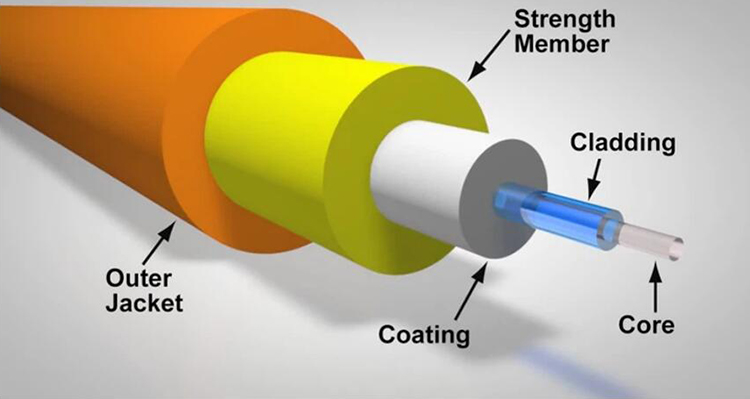
Are you ready to enhance your network’s performance with a fiber optic connection? Discover a step-by-step guide on how to connect your fiber cable to an SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) port. This detailed article will walk you through the process, ensuring you achieve a stable and high-speed network connection.
Fiber Cable, SFP Port, Network Connection, Fiber Optic, Step-by-Step Guide, Data Transmission, Networking Equipment
Understanding the Basics and Preparing for the Connection
When it comes to modern networking, fiber optics and SFP ports play crucial roles in ensuring efficient data transmission. Before diving into the actual connection process, it’s essential to understand the basic concepts and prepare adequately. This preparation ensures a smooth setup and optimal performance of your network.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an SFP Port?
An SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) port is a compact, hot-swappable transceiver used in networking hardware to connect network devices like switches, routers, and servers. SFP ports are designed to accommodate various types of modules, allowing for different types of connections, such as fiber optic or copper cables. Fiber optic SFP modules are particularly valued for their ability to support high-speed, long-distance data transmission.
Why Use Fiber Optic Cables?
Fiber optic cables are renowned for their high bandwidth and long-distance transmission capabilities. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optics use light to transmit data, which minimizes signal degradation and offers superior speed and reliability. They are particularly useful in scenarios where large amounts of data need to be transmitted over long distances, making them ideal for enterprise networks and data centers.
Preparing for the Connection
Before you begin the connection process, ensure that you have the following:
- Fiber Optic Cable: Ensure you have the correct type of fiber optic cable (single-mode or multi-mode) that matches the SFP module and network requirements.
- SFP Module: Verify that you have the appropriate SFP module for your network’s needs. Different SFP modules support different types of fiber (LC, SC, ST) and transmission distances.
- Clean Work Environment: Fiber optic cables are sensitive to dust and debris, which can affect performance. Work in a clean, dust-free environment to ensure a successful connection.
Anti-Static Precautions: Use anti-static wrist straps and work on an anti-static mat to prevent damage to sensitive components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Fiber Cable to an SFP Port
Turn Off Power: For safety reasons, turn off the power to your networking equipment before connecting or disconnecting any cables. This helps prevent potential damage to the hardware and ensures a safe working environment.
- Locate the SFP Port: Identify the SFP port on your networking device. This port is usually labeled and is designed to accommodate SFP modules.
- Insert the SFP Module: If your SFP module is not already installed in the SFP port, gently insert it into the slot until it clicks into place. Ensure that it is properly seated and secure.
- Inspect the Fiber Optic Cable: Examine the fiber optic cable to ensure there are no visible signs of damage or contamination. Clean the connectors if necessary using a fiber optic cleaning kit.
- Connect the Fiber Cable: Align the fiber optic cable with the SFP module’s connector and gently insert it. Ensure that the cable is fully inserted and securely connected.
- Power On Equipment: Once the fiber optic cable is connected, power on your networking equipment and check for any indicator lights on the SFP module. These lights typically signal successful connectivity and data transmission.
- Verify the Connection: Use network management tools or diagnostic software to verify that the connection is working correctly. Check for any error messages or connectivity issues and resolve them if necessary.
Troubleshooting and Optimizing Your Connection
Even with a seemingly perfect connection, issues can sometimes arise. In this section, we will explore common troubleshooting steps and tips for optimizing your fiber optic connection to ensure maximum performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
No Signal or Connectivity Problems: If you’re not getting a signal, check the following:
Ensure that the fiber optic cable is properly connected to both the SFP module and the corresponding port on the other end.
Inspect the fiber optic cable for any signs of damage or bending that could affect signal transmission.
Verify that the SFP module is correctly inserted and fully seated in the port.
Check for Indicator Lights: Most SFP modules have LED indicators that show the status of the connection. If these lights are off or showing error patterns, refer to the module’s documentation for troubleshooting information.
Clean Connectors: Contamination on the fiber optic connectors can cause signal degradation. Use a fiber optic cleaning kit to gently clean the connectors and ensure a clear optical path.
Test with a Different Cable or Module: If you suspect that the issue lies with the cable or module, try using a different fiber optic cable or SFP module to identify the problem.
Optimizing Your Fiber Optic Connection
Ensure Proper Alignment: Proper alignment of the fiber optic cable with the SFP module is crucial for optimal performance. Avoid sharp bends in the cable and ensure a secure connection to minimize signal loss.
Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean fiber optic cables and connectors to maintain performance. Scheduled maintenance helps prevent issues related to dust and wear over time.
Monitor Network Performance: Utilize network monitoring tools to keep an eye on performance metrics. This helps you identify any issues early and take corrective actions before they affect network operations.
Upgrade Components if Necessary: As technology evolves, consider upgrading your SFP modules and fiber optic cables to keep pace with increasing data demands and to ensure compatibility with newer networking standards.
Consult Documentation and Support: Refer to the documentation provided by the manufacturers of your SFP modules and networking equipment for specific troubleshooting and optimization tips. If issues persist, don’t hesitate to reach out to technical support for assistance.
Conclusion
Connecting fiber optic cables to SFP ports may seem complex, but with the right knowledge and preparation, you can achieve a reliable and high-speed network connection. By understanding the basics of SFP ports and fiber optics, preparing your equipment properly, and following our step-by-step guide, you’ll be well on your way to setting up a robust network infrastructure. Remember to troubleshoot effectively and optimize your connection to ensure long-term performance and reliability. Happy networking!